Generation of 2-mode scale-free graphs for link-level internet topology modeling
- PMID: 33166286
- PMCID: PMC7652253
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240100
Generation of 2-mode scale-free graphs for link-level internet topology modeling
Abstract
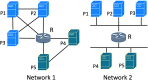
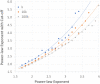
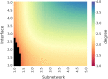
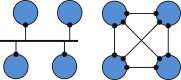
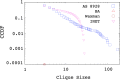
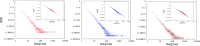
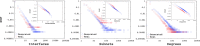
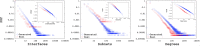
Comprehensive analysis that aims to understand the topology of real-world networks and the development of algorithms that replicate their characteristics has been significant research issues. Although the accuracy of newly developed network protocols or algorithms does not depend on the underlying topology, the performance generally depends on the topology. As a result, network practitioners have concentrated on generating representative synthetic topologies and utilize them to investigate the performance of their design in simulation or emulation environments. Network generators typically represent the Internet topology as a graph composed of point-to-point links. In this study, we discuss the implications of multi-access links on the synthetic network generation and modeling of the networks as bi-partite graphs to represent both subnetworks and routers. We then analyze the characteristics of sampled Internet topology data sets from backbone Autonomous Systems (AS) and observe that in addition to the commonly recognized power-law node degree distribution, the subnetwork size and the router interface distributions often exhibit power-law characteristics. We introduce a SubNetwork Generator (SubNetG) topology generation approach that incorporates the observed measurements to produce bipartite network topologies. In particular, generated topologies capture the 2-mode relation between the layer-2 (i.e., the subnetwork and interface distributions) and the layer-3 (i.e., the degree distribution) that is missing from the current network generators that produce 1-mode graphs. The SubNetG source code and experimental data is available at https://github.com/netml/sonet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures










References
-
- Pastor-Satorras R., Vespignani A., Evolution and Structure of the Internet: A Statistical Physics Approach, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 2004. 10.1017/CBO9780511610905 - DOI
-
- Newman M., Networks: An Introduction, Oxford University Press, Inc, 2010
-
- Gunes M. H., Bilir S., Sarac K., Korkmaz T., A measurement study on overhead distribution of value-added internet services, Computer Networks, Volume 51, Issue 14, 2007, Pages 4153–4173. 10.1016/j.comnet.2007.05.001 - DOI
-
- L. Cheng, N.C. Hutchinson, M. R. Ito, RealNet: A Topology Generator Based on Real Internet Topology, 22nd International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications—Workshops (AINA workshops 2008), Okinawa, 2008, pp. 526-532. 10.1109/WAINA.2008.66 - DOI
-
- N. Hidaka, S. Arakawa, M. Murata, A Modeling Method for ISP Topologies Based on Network-Cost Optimization, Fourth International Conference on Autonomic and Autonomous Systems (ICAS’08), Gosier, 2008, pp. 169-174. 10.1109/ICAS.2008.7 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

