Erectile dysfunction drugs altered the activities of antioxidant enzymes, oxidative stress and the protein expressions of some cytochrome P450 isozymes involved in the steroidogenesis of steroid hormones
- PMID: 33166302
- PMCID: PMC7652355
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241509
Erectile dysfunction drugs altered the activities of antioxidant enzymes, oxidative stress and the protein expressions of some cytochrome P450 isozymes involved in the steroidogenesis of steroid hormones
Abstract
Objectives: Infertility is a global health problem with about 15 percent of couples involved. About half of the cases of infertility are related to male-related factors. A major cause of infertility in men is oxidative stress, which refers to an imbalance between levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants. Erectile dysfunction drugs (EDD), known as phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDEIs), have been used for the treatment of ED. It has been shown that oxidative stress plays an important role in the progression of erectile dysfunction. Oxidative stress can be alleviated or decreased by non-antioxidants and antioxidant enzymes. The present study was undertaken to determine if these compounds could have a role in the incidence of infertility, especially after long-term use. Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the effect of EDD on the activities of antioxidant enzymes, free radical levels as well as the protein expression of different cytochrome P450 isozymes involved in the steroidogenesis of different hormones. In addition, the activity of both 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 17-ketosteroid reductase were assayed. The architectures of both livers and testes cells were investigated under the influence of EDD.
Methods: A daily dose of Sildenafil (1.48 mg/kg), Tadalafil (0.285 mg/kg) and Vardenafil (0.285 mg/kg) were administered orally to male rabbits for 12 week. Western immunoblotting, ELISA, spectrophotometric and histopathological techniques were used in this study.
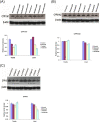
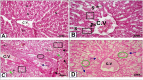
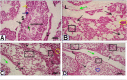
Results: The present study showed that Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil treatments significantly decreased the levels of glutathione and free radicals in both livers and testes of rabbits. Also, Vardenafil and Sildenafil induced the activity of superoxide dismutase and catalase whereas, glutathione S-transferase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione peroxidase activities inhibited in livers of rabbits. The protein expression of cytochrome P450 isozymes (CYP 11A1, 21A2, and 19C) which are involved in the steroidogenesis was markedly changed in both livers and testes of rabbits after their treatments for 12 weeks. After the treatment of rabbits with these medication, the protein expression of CYP11A1 was slightly down-regulated in both livers and testes except Sildenafil up-regulated such protein expression. In addition, the protein expressions of CYP11A1 and CYP 19C in both livers and testes were down-regulated after treatment of rabbits with Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil for 12 weeks. Also, these drugs inhibited the activity of both 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 17-ketosteroid reductase in testes of rabbits. Moreover, Sildenafil, Vardenafil, and Tadalafil-treated rabbits showed a decrease in spermatocytes and the number of sperms in the testes.
Conclusions: It is concluded that ED drugs induced the activities of both SOD and catalase which consequently decreased MDA level. Decrement in MDA levels and oxidative stress could therefore sustain the erection for a long period of time. On the other hand, it is not advised to use these drugs for a long-term since the protein expressions of CYP isozymes involved in steroidogenesis as well as the numbers of spermatocytes in testes were decreased.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Changed the Protein Expressions and Activities of Drug-Metabolising Enzymes in the Liver of Male Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:4970906. doi: 10.1155/2016/4970906. Epub 2016 Oct 9. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27800121 Free PMC article.
-
Erectile dysfunction drugs and oxidative stress in the liver of male rats.Toxicol Rep. 2015 Jun 6;2:933-938. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.06.002. eCollection 2015. Toxicol Rep. 2015. PMID: 28962432 Free PMC article.
-
N-nitrosamines induced infertility and hepatotoxicity in male rabbits.Environ Toxicol. 2017 Sep;32(9):2212-2220. doi: 10.1002/tox.22436. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Environ Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28573719
-
[Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: past, present and future].Urologiia. 2017 Apr;(1):103-107. doi: 10.18565/urol.2017.1.103-107. Urologiia. 2017. PMID: 28394532 Review. Russian.
-
Comparison of clinical trials with sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil in erectile dysfunction.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Jan;6(1):75-84. doi: 10.1517/14656566.6.1.75. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 15709885 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of biological landscape of oxidative stress-related genes in diabetic erectile dysfunction.Int J Impot Res. 2024 Sep;36(6):627-635. doi: 10.1038/s41443-023-00814-1. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Int J Impot Res. 2024. PMID: 38145980
-
Beneficial Effect of Methanolic Extract of Frankincense (Boswellia Sacra) on Testis Mediated through Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis.Molecules. 2022 Jul 22;27(15):4699. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154699. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35897864 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and Erectile Dysfunction: Pathophysiology, Impacts, and Potential Treatments.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 14;46(8):8807-8834. doi: 10.3390/cimb46080521. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39194738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of male erectile dysfunction: From the past to the future.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 27;14:1148834. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1148834. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36923224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan Nanoparticles Alleviated the Adverse Effects of Sildenafil on the Oxidative Stress Markers and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Rats.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Jan 31;2023:9944985. doi: 10.1155/2023/9944985. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36891377 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

