Evaluation of the sublethal effect of tetrachlorantraniliprole on Spodoptera exigua and its potential toxicity to two non-target organisms
- PMID: 33166345
- PMCID: PMC7652279
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242052
Evaluation of the sublethal effect of tetrachlorantraniliprole on Spodoptera exigua and its potential toxicity to two non-target organisms
Abstract
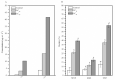
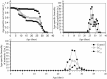
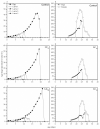
Tetrachlorantraniliprole (TCAP) is a novel anthranilic diamide insecticide that specifically targets the ryanodine receptors of lepidopteran insect species with excellent insecticidal activity. Previous studies have reported the sublethal effects of multiple diamides on several lepidopteran species, whereas the sublethal and non-target effects of TCAP remain largely unknown. We assessed the sublethal effects of TCAP on Spodoptera exigua. We also investigated the effects of TCAP on non-target Harmonia axyridis and Eisenia fetida, S. exigua was more sensitive to TCAP than to chlorantraniliprole, as the LC50 (10.371 μg L-1 at 72 h) of TCAP was relatively lower. Compared with those of the control, sublethal concentrations of TCAP (LC10 and LC30) not only prolonged the duration of the larval and pupal stages as well as the mean generation time but also reduced certain population parameters. On the other hand, TCAP exposure, even at the highest concentration, did not induce toxic effects in H. axyridis ladybugs (1st instar larvae and adults) or E. fetida earthworms. Taken together, our results suggest that TCAP can be used as a novel and promising component of the integrated pest management (IPM) program against S. exigua due to its robust target effects and negligible non-target risks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lethal and sublethal effects of spinosad on Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J Econ Entomol. 2013 Aug;106(4):1825-31. doi: 10.1603/ec12220. J Econ Entomol. 2013. PMID: 24020299
-
Toxicity and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on the development and fecundity of a non-specific predator, the multicolored Asian lady beetle, Harmonia axyridis (Pallas).Chemosphere. 2017 Jul;178:496-503. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.082. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Chemosphere. 2017. PMID: 28347913
-
Lethal and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on Spodoptera cosmioides (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).Pest Manag Sci. 2018 Dec;74(12):2817-2821. doi: 10.1002/ps.5070. Epub 2018 Aug 12. Pest Manag Sci. 2018. PMID: 29766638
-
Chronic sublethal exposure to chlorantraniliprole inhibits growth and development by disrupting the sugar and fatty acid metabolism in Spodoptera frugiperda.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025 Mar;208:106302. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2025.106302. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40015894
-
Sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on growth, biochemical and molecular parameters in two chironomids, Chironomus kiiensis and Chironomus javanus.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023 Mar 15;253:114658. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114658. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023. PMID: 36796207 Review.
Cited by
-
Dose Effects of Flubendiamide and Thiodicarb against Spodoptera Species Developing on Bt and Non-Bt Soybean.Insects. 2023 Sep 14;14(9):766. doi: 10.3390/insects14090766. Insects. 2023. PMID: 37754734 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analyses of the effects of sublethal doses of emamectin benzoate and tetrachlorantraniliprole on the gut microbiota of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).J Insect Sci. 2023 Jul 1;23(4):7. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/iead039. J Insect Sci. 2023. PMID: 37471131 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity and Sublethal Effects of Diamide Insecticides on Key Non-Target Natural Predators, the Larvae of Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae).Toxics. 2023 Mar 16;11(3):270. doi: 10.3390/toxics11030270. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 36977035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Metcalf RL, Metcalf RA. In: Destructive and useful insects: their habits and control, fifth ed McGrawHill, San Francisco, USA, 1992; 490.
-
- Ahmad M, Farid A, Saeed M. Resistance to new insecticides and their synergism in Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from Pakistan. Crop Prot. 2018; 107: 79–86. 10.1016/j.cropro.2017.12.028 - DOI
-
- Kinney CA, Campbell BR, Thompson R, Furlong ET, Kolpin DW, Burkhardt MR. Earthworm bioassays and seedling emergence for monitoring toxicity, aging and bioaccumulation of anthropogenic waste indicator compounds in bio solids-amended soil. Sci Total Environ. 2012; 433: 507–515. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.06.097 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vasantha-Srinivasan P, Senthil-Nathan S, Ponsankar A, Thanigaivel A, Chellappandian M, Edwin ES, et al. Acute toxicity of chemical pesticides and plant-derived essential oil on the behavior and development of earthworms, Eudrilus eugeniae (Kinberg) and Eisenia fetida (Savigny). Environ Sci Pollu Res. 2018; 25(11): 10371–10382. 10.1007/s11356-017-9236-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

