The TFIIH subunits p44/p62 act as a damage sensor during nucleotide excision repair
- PMID: 33166411
- PMCID: PMC7736792
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa973
The TFIIH subunits p44/p62 act as a damage sensor during nucleotide excision repair
Abstract
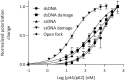
Nucleotide excision repair (NER) in eukaryotes is orchestrated by the core form of the general transcription factor TFIIH, containing the helicases XPB, XPD and five 'structural' subunits, p62, p44, p34, p52 and p8. Recent cryo-EM structures show that p62 makes extensive contacts with p44 and in part occupies XPD's DNA binding site. While p44 is known to regulate the helicase activity of XPD during NER, p62 is thought to be purely structural. Here, using helicase and adenosine triphosphatase assays we show that a complex containing p44 and p62 enhances XPD's affinity for dsDNA 3-fold over p44 alone. Remarkably, the relative affinity is further increased to 60-fold by dsDNA damage. Direct binding studies show this preference derives from p44/p62's high affinity (20 nM) for damaged ssDNA. Single molecule imaging of p44/p62 complexes without XPD reveals they bind to and randomly diffuse on DNA, however, in the presence of UV-induced DNA lesions these complexes stall. Combined with the analysis of a recent cryo-EM structure, we suggest that p44/p62 acts as a novel DNA-binding entity that enhances damage recognition in TFIIH. This revises our understanding of TFIIH and prompts investigation into the core subunits for an active role during DNA repair and/or transcription.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lack of CAK complex accumulation at DNA damage sites in XP-B and XP-B/CS fibroblasts reveals differential regulation of CAK anchoring to core TFIIH by XPB and XPD helicases during nucleotide excision repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2012 Dec 1;11(12):942-50. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Oct 17. DNA Repair (Amst). 2012. PMID: 23083890 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles for the XPB/p52 and XPD/p44 subcomplexes of TFIIH in damaged DNA opening during nucleotide excision repair.Mol Cell. 2007 Apr 27;26(2):245-56. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.03.009. Mol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17466626
-
XPB and XPD helicases in TFIIH orchestrate DNA duplex opening and damage verification to coordinate repair with transcription and cell cycle via CAK kinase.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 Jul 15;10(7):697-713. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.04.028. Epub 2011 May 14. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21571596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of TFIIH activation for nucleotide excision repair.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 28;10(1):2885. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10745-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31253769 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide Excision Repair: Insights into Canonical and Emerging Functions of the Transcription/DNA Repair Factor TFIIH.Genes (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;16(2):231. doi: 10.3390/genes16020231. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40004560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA bridges: A novel platform for single-molecule sequencing and other DNA-protein interaction applications.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 22;16(11):e0260428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260428. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34807931 Free PMC article.
-
Every protagonist has a sidekick: Structural aspects of human xeroderma pigmentosum-binding proteins in nucleotide excision repair.Protein Sci. 2021 Nov;30(11):2187-2205. doi: 10.1002/pro.4173. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 34420242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of the Tfb1 pleckstrin homology domain with Rad2 and Rad4 in transcription coupled and global genomic nucleotide excision repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jun 24;52(11):6333-6346. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae286. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38634797 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution cryo-EM structures of TFIIH and their functional implications.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019 Dec;59:188-194. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2019.08.002. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019. PMID: 31600675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular architecture and functional dynamics of the pre-incision complex in nucleotide excision repair.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 1;15(1):8511. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52860-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39353945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coin F., Oksenych V., Egly J.M.. Distinct roles for the XPB/p52 and XPD/p44 subcomplexes of TFIIH in damaged DNA opening during nucleotide excision repair. Mol. Cell. 2007; 26:245–256. - PubMed
-
- Roy R., Schaeffer L., Humbert S., Vermeulen W., Weeda G., Egly J.M.. The DNA-dependent ATPase activity associated with the class II basic transcription factor BTF2/TFIIH. J. Biol. Chem. 1994; 269:9826–9832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/P00847X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/M019144/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I003460/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/M01603X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

