Cre/LoxP-HBV plasmids generating recombinant covalently closed circular DNA genome upon transfection
- PMID: 33166564
- PMCID: PMC7779077
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198224
Cre/LoxP-HBV plasmids generating recombinant covalently closed circular DNA genome upon transfection
Abstract
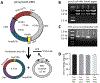
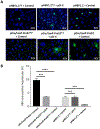
New therapies against hepatitis B virus (HBV) require the elimination of covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA), the episomal HBV genome. HBV plasmids containing an overlength 1.3-mer genome and bacterial backbone (pHBV1.3) are used in many different models, but do not replicate the unique features of cccDNA. Since the stable cccDNA pool is a barrier to HBV eradication in patients, we developed a recombinant circular HBV genome (rcccDNA) to mimic the cccDNA using Cre/LoxP technology. We validated four LoxP insertion sites into the HBV genome using hydrodynamic tail vein injection into murine liver, demonstrating high levels of HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and HBV DNA expression with rcccDNA formation. HBsAg expression from rcccDNA was >30,000 ng/mL over 78 days, while HBsAg-expression from pHBV1.3 plasmid DNA declined from 2753 ng/mL to 131 ng/mL over that time in immunodeficient mice (P < 0.001), reflective of plasmid DNA silencing. We then cloned Cre-recombinase in cis on the LoxP-HBV plasmids, achieving plasmid stability in bacteria with intron insertion into Cre and demonstrating rcccDNA formation after transfection in vitro and in vivo. These cis-Cre/LoxP-HBV plasmids were then used to create HBx-mutant and GFP reporter plasmids to further probe cccDNA biology and antiviral strategies against cccDNA. Overall, we believe these auto-generating rcccDNA plasmids will be of great value to model cccDNA for testing new therapies against HBV infection.
Keywords: Cre/LoxP; Drug discovery; HBV; cccDNA.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Establishment of Cre-mediated HBV recombinant cccDNA (rcccDNA) cell line for cccDNA biology and antiviral screening assays.Antiviral Res. 2018 Apr;152:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.02.007. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Antiviral Res. 2018. PMID: 29432776
-
The Cre/loxP-Based Recombinant HBV cccDNA System In Vitro and In Vivo.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2837:185-198. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4027-2_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39044085
-
A novel recombinant cccDNA-based mouse model with long term maintenance of rcccDNA and antigenemia.Antiviral Res. 2020 Aug;180:104826. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104826. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Antiviral Res. 2020. PMID: 32502604
-
New Insights on Molecular Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Formation.Cells. 2020 Nov 6;9(11):2430. doi: 10.3390/cells9112430. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33172220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attacking hepatitis B virus cccDNA--The holy grail to hepatitis B cure.J Hepatol. 2016 Apr;64(1 Suppl):S41-S48. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.02.009. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27084036 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in gene editing technologies for probiotic-enabled disease therapy.iScience. 2024 Aug 22;27(9):110791. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110791. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39286511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrodynamic Delivery: Characteristics, Applications, and Technological Advances.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 31;15(4):1111. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041111. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress of Infection and Replication Systems of Hepatitis B Virus.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Jun 4;7(6):1711-1721. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00147. eCollection 2024 Jun 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38898948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A hepatitis B virus transgenic mouse model with a conditional, recombinant, episomal genome.JHEP Rep. 2021 Feb 6;3(2):100252. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100252. eCollection 2021 Apr. JHEP Rep. 2021. PMID: 33733079 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Mouse Models for Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Their Application.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 29;12:766534. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.766534. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34777385 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Billioud G, Kruse RL, Carrillo M, Whitten-Bauer C, Gao D, Kim A, Chen L, McCaleb ML, Crosby JR, Hamatake R, Hong Z, Garaigorta U, Swayze E, Bissig K-D, Wieland S, 2016. In vivo reduction of hepatitis B virus antigenemia and viremia by antisense oligonucleotides. Journal of Hepatology 64, 781–789. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.032 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Z-Y, He C-Y, Ehrhardt A, Kay MA, 2003. Minicircle DNA vectors devoid of bacterial DNA result in persistent and high-level transgene expression in vivo. Mol Ther 8, 495–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

