AHR Signaling Interacting with Nutritional Factors Regulating the Expression of Markers in Vascular Inflammation and Atherogenesis
- PMID: 33167400
- PMCID: PMC7663825
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21218287
AHR Signaling Interacting with Nutritional Factors Regulating the Expression of Markers in Vascular Inflammation and Atherogenesis
Abstract
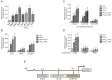
There is strong evidence that exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and a high-fat diet (HFD) increase the risk of mortality from atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies indicate that PM2.5 generated by combustion activates the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR) and inflammatory cytokines contributing to PM2.5-mediated atherogenesis. Here we investigate the effects of components of a HFD on PM-mediated activation of AHR in macrophages. Cells were treated with components of a HFD and AHR-activating PM and the expression of biomarkers of vascular inflammation was analyzed. The results show that glucose and triglyceride increase AHR-activity and PM2.5-mediated induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP)1A1 mRNA in macrophages. Cholesterol, fructose, and palmitic acid increased the PM- and AHR-mediated induction of proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages. Treatment with palmitic acid significantly increased the expression of inflammatory cytokines and markers of vascular injury in human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) after treatment with PM2.5. The PM2.5-mediated activation of the atherogenic markers C-reactive protein (CRP) and S100A9, a damage-associated molecular pattern molecule, was found to be AHR-dependent and involved protein kinase A (PKA) and a CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) binding element. This study identified nutritional factors interacting with AHR signaling and contributing to PM2.5-induced markers of atherogenesis and future cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: AHR; PM; TCDD; atherosclerosis; cytokines; inflammation; macrophages; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
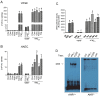
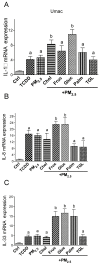

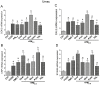
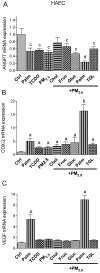


References
-
- Rückerl R., Greven S., Ljungman P., Aalto P., Antoniades C., Bellander T., Berglind N., Chrysohoou C., Forastiere F. Air pollution and inflammation (interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, fibrinogen) in myocardial infarction survivors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007;115:1072–1080. doi: 10.1289/ehp.10021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

