Is there a 24-hour rhythm in alcohol craving and does it vary by sleep/circadian timing?
- PMID: 33167734
- PMCID: PMC7855555
- DOI: 10.1080/07420528.2020.1838532
Is there a 24-hour rhythm in alcohol craving and does it vary by sleep/circadian timing?
Abstract
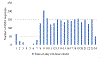
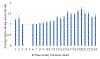
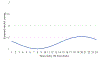
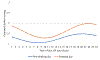
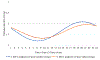
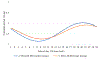
Increasing evidence implicates sleep/circadian factors in alcohol use; however, the role of such factors in alcohol craving has received scant attention. Prior research suggests a 24-hour rhythm in related processes (e.g., reward motivation), but more research directly investigating a rhythm in craving is needed. Moreover, prior evidence is ambiguous whether such a rhythm in alcohol craving may vary by sleep/circadian timing. To examine these possibilities, 36 late adolescents (18-22 years of age; 61% female) with regular alcohol use but without a current alcohol use disorder were recruited to complete smartphone reports of alcohol craving intensity six times a day for two weeks. During these two weeks, participants wore wrist actigraphs and completed two in-lab assessments (on Thursday and Sunday) of dim light melatonin onset (DLMO). Average actigraphically derived midpoint of sleep on weekends and average DLMO were used as indicators of sleep and circadian timing, respectively. Multilevel cosinor analysis revealed a 24-hour rhythm in alcohol craving. Findings across the sleep and circadian timing variables converged to suggest that sleep/circadian timing moderated the 24-hour rhythm in alcohol craving. Specifically, people with later sleep/circadian timing had later timing of peak alcohol craving. These findings add to the growing evidence of potential circadian influences on reward-related phenomena and suggest that greater consideration of sleep and circadian influences on alcohol craving may be useful for understanding alcohol use patterns and advancing related interventions.
Keywords: Alcohol; actigraphy; alcohol craving; chronotype; circadian rhythm; dim light melatonin onset; diurnal rhythm; ecological momentary assessment; midpoint of sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTEREST
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arfken CL. 1988. Temporal pattern of alcohol consumption in the United States. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 12(1):137–142. - PubMed
-
- Byrne JEM, Murray G. 2017. Diurnal rhythms in psychological reward functioning in healthy young men: ‘Wanting’, liking, and learning. Chronobiol Int. 34(2):287–295. - PubMed
-
- Crowley SJ, Acebo C, Fallone G, Carskadon MA. 2006. Estimating Dim Light Melatonin Onset (DLMO) phase in adolescents using summer or school-year sleep/wake schedules. Sleep. 29(12):1632–1641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
