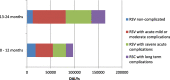
Disability-adjusted life years for respiratory syncytial virus in children under 2 years
- PMID: 33167966
- PMCID: PMC7654061
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-09796-x
Disability-adjusted life years for respiratory syncytial virus in children under 2 years
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus infection is the leading cause of bronchiolitis in Colombia. There is growing evidence about the impact of Respiratory syncytial virus on society in terms of years of life lost due to this condition. The objective of the present study is to determine the Disability-Adjusted Life Years for respiratory syncytial virus in children under 2 years in Colombia.
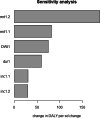
Methods: Data from the national epidemiological surveillance system were used to estimate DALYs, calculated from the sum of years of life lost and years lived with disability due to RSV infection in Colombia. A bootstrapped method with 10,000 iterations was used to estimate each statistical parameter using the package DALY calculator in R.
Results: In 2019, 260,873 years of life (CI95% 208,180-347,023) were lost due to RSV bronchiolitis in Colombian children under 2 years. The estimated rate was 20 DALYs / 1000 person-year (95% CI 16-27).
Conclusion: This is the first report estimating the impact of RSV bronchiolitis morbidity and mortality in Colombia. The findings of the present study suggest that the actual burden and cost of bronchiolitis due to RSV is high. Prevention strategies, such as RSV vaccination, to reduce morbidity associated with RSV infection should be encouraged in our country.
Keywords: Colombia; Global burden of disease; Respiratory syncytial virus.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disability-adjusted life years for acute bronchiolitis in infants in Colombia.Pan Afr Med J. 2021 Aug 12;39:236. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.39.236.25761. eCollection 2021. Pan Afr Med J. 2021. PMID: 34659609 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Effects of Active Immunisation against Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) using Decision-Analytic Models: A Systematic Review with a Focus on Vaccination Strategies, Modelling Methods and Input Data.Pharmacoeconomics. 2021 Mar;39(3):287-315. doi: 10.1007/s40273-020-00991-7. Epub 2021 Jan 19. Pharmacoeconomics. 2021. PMID: 33462760 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus infection as a cause of hospitalization in population under 1 year in Colombia.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2013 Nov-Dec;89(6):544-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2013. PMID: 24029550
-
Health and economic burden of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease and the cost-effectiveness of potential interventions against RSV among children under 5 years in 72 Gavi-eligible countries.BMC Med. 2020 Apr 6;18(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01537-6. BMC Med. 2020. PMID: 32248817 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus: an underestimated cause of respiratory infection, with prospects for a vaccine.Commun Dis Public Health. 1999 Dec;2(4):234-41. Commun Dis Public Health. 1999. PMID: 10598379 Review.
Cited by
-
Budget impact analysis of surfactant therapy for bronchiolitis in critically ill infants: the Colombian National Health System perspective.BMC Health Serv Res. 2021 Apr 13;21(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s12913-021-06347-x. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021. PMID: 33849521 Free PMC article.
-
The cost-effectiveness of hypertonic saline inhalations for infant bronchiolitis.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Nov 2;20(1):1001. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05814-1. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 33138807 Free PMC article.
-
Disability-adjusted life years for acute bronchiolitis in infants in Colombia.Pan Afr Med J. 2021 Aug 12;39:236. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.39.236.25761. eCollection 2021. Pan Afr Med J. 2021. PMID: 34659609 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of twelve immunization-preventable infectious diseases on population health using disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in Spain.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 5;24(1):779. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09637-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39103777 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of RSV Hospitalization on Children's Quality of Life.Diseases. 2023 Aug 30;11(3):111. doi: 10.3390/diseases11030111. Diseases. 2023. PMID: 37754307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nair H, Nokes DJ, Gessner BD, Dherani M, Madhi SA, Singleton RJ, et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;375(9725):1545–1555. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60206-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hall CB, Simoes EA, Anderson LJ. Clinical and epidemiologic features of respiratory syncytial virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013;372:39–57. - PubMed
-
- Peñaloza R, Salamanca B, Rodriguez J, Beltran A. Estimación de la carga de enfermedad para Colombia, 2010. 2014(Editorial Pontificia Universidad Javeriana).
-
- Mathers CD VT, Lopez AD, Salomon J, Ezzati M. National Burden of Disease Studies: A Practical Guide: Global Program on Evidence for Health Policy. Geneva: World Health Organization.; 2001 [Available from: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/nationalburdenofdiseasemanual.pdf.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical