An automated oxystat fermentation regime for microoxic cultivation of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense
- PMID: 33168043
- PMCID: PMC7654035
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-020-01469-z
An automated oxystat fermentation regime for microoxic cultivation of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense
Abstract
Background: Magnetosomes produced by magnetotactic bacteria represent magnetic nanoparticles with unprecedented characteristics. However, their use in many biotechnological applications has so far been hampered by their challenging bioproduction at larger scales.
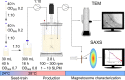
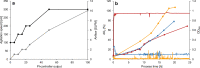
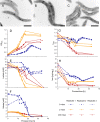
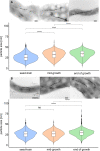
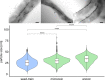
Results: Here, we developed an oxystat batch fermentation regime for microoxic cultivation of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense in a 3 L bioreactor. An automated cascade regulation enabled highly reproducible growth over a wide range of precisely controlled oxygen concentrations (1-95% of air saturation). In addition, consumption of lactate as the carbon source and nitrate as alternative electron acceptor were monitored during cultivation. While nitrate became growth limiting during anaerobic growth, lactate was the growth limiting factor during microoxic cultivation. Analysis of microoxic magnetosome biomineralization by cellular iron content, magnetic response, transmission electron microscopy and small-angle X-ray scattering revealed magnetosomal magnetite crystals were highly uniform in size and shape.
Conclusion: The fermentation regime established in this study facilitates stable oxygen control during culturing of Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. Further scale-up seems feasible by combining the stable oxygen control with feeding strategies employed in previous studies. Results of this study will facilitate the highly reproducible laboratory-scale bioproduction of magnetosomes for a diverse range of future applications in the fields of biotechnology and biomedicine.
Keywords: Magnetosome biomineralization; Magnetosomes; Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense; Oxystat fermentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lohße A, Ullrich S, Katzmann E, Borg S, Wanner G, Richter M, Voigt B, Schweder T, Schüler D. Functional analysis of the magnetosome island in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense: the mamAB operon is sufficient for magnetite biomineralization. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e25561. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025561. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lohße A, Borg S, Raschdorf O, Kolinko I, Tompa É, Pósfai M, Faivre D, Baumgartner J, Schüler D. Genetic dissection of the mamAB and mms6 operons reveals a gene set essential for magnetosome biogenesis in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. J Bacteriol. 2014;196:2658–2669. doi: 10.1128/JB.01716-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

