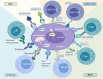
Emerging agents and regimens for multiple myeloma
- PMID: 33168044
- PMCID: PMC7654052
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00980-5
Emerging agents and regimens for multiple myeloma
Abstract
The outcomes of multiple myeloma (MM) have been improved significantly with the therapies incorporating proteasome inhibitors (PI), immunomodulatory drugs, monoclonal antibodies (MoAb) and stem cell transplantation. However, relapsed and refractory MM (RRMM) remains a major challenge. Novel agents and regimens are under active clinical development. These include new PIs such as ixazomib, marizomib, and oprozomib; new MoAbs such as isatuximab and MOR202; novel epigenetic agent ricolinostat and novel cytokines such as siltuximab. Recently, the first XPO-1 inhibitor, selinexor, was approved for RRMM. BCMA-targeted BiTE, antibody-drug conjugates and CAR-T cells have the potential to revolutionize the therapy for RRMM. In this review, we summarized the latest clinical development of these novel agents and regimens.
Keywords: BiTE; CAR-T; Checkpoint inhibitor; Immunotherapy; Monoclonal antibody; Multiple myeloma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Durie BGM, Hoering A, Abidi MH, Rajkumar SV, Epstein J, Kahanic SP, et al. Bortezomib with lenalidomide and dexamethasone versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone alone in patients with newly diagnosed myeloma without intent for immediate autologous stem-cell transplant (SWOG S0777): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10068):519–527. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31594-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous