SVFX: a machine learning framework to quantify the pathogenicity of structural variants
- PMID: 33168059
- PMCID: PMC7650198
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-020-02178-x
SVFX: a machine learning framework to quantify the pathogenicity of structural variants
Abstract
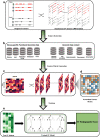
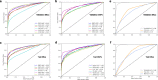
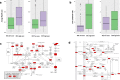
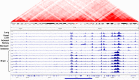
There is a lack of approaches for identifying pathogenic genomic structural variants (SVs) although they play a crucial role in many diseases. We present a mechanism-agnostic machine learning-based workflow, called SVFX, to assign pathogenicity scores to somatic and germline SVs. In particular, we generate somatic and germline training models, which include genomic, epigenomic, and conservation-based features, for SV call sets in diseased and healthy individuals. We then apply SVFX to SVs in cancer and other diseases; SVFX achieves high accuracy in identifying pathogenic SVs. Predicted pathogenic SVs in cancer cohorts are enriched among known cancer genes and many cancer-related pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Li Y, Roberts ND, Wala JA, Shapira O, Schumacher SE, Kumar K, et al. Patterns of somatic structural variation in human cancer genomes. Nature [Internet]. Nature Research. 2020;578:112–21. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32025012/. [cited 2020 Oct 20]. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

