FDA Approval Summary: Alpelisib Plus Fulvestrant for Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 33168657
- PMCID: PMC8535764
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3652
FDA Approval Summary: Alpelisib Plus Fulvestrant for Patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative, PIK3CA-mutated, Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
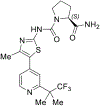
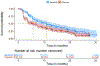
On May 24, 2019, the FDA granted regular approval to alpelisib in combination with fulvestrant for postmenopausal women, and men, with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2-negative, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA)-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer as detected by an FDA-approved test following progression on or after an endocrine-based regimen. Approval was based on the SOLAR-1 study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of alpelisib plus fulvestrant versus placebo plus fulvestrant. The primary endpoint was investigator-assessed progression-free survival (PFS) per RECIST v1.1 in the cohort of trial participants whose tumors had a PIK3CA mutation. The estimated median PFS by investigator assessment in the alpelisib plus fulvestrant arm was 11 months [95% confidence interval (CI), 7.5-14.5] compared with 5.7 months (95% CI, 3.7-7.4) in the placebo plus fulvestrant arm (HR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.50-0.85; two-sided P = 0.001). The median overall survival was not yet reached for the alpelisib plus fulvestrant arm (95% CI, 28.1-NE) and was 26.9 months (95% CI, 21.9-NE) for the fulvestrant control arm. No PFS benefit was observed in trial participants whose tumors did not have a PIK3CA mutation (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.58-1.25). The most common adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, on the alpelisib plus fulvestrant arm were increased glucose, increased creatinine, diarrhea, rash, decreased lymphocyte count, increased gamma glutamyl transferase, nausea, increased alanine aminotransferase, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, increased lipase, decreased appetite, stomatitis, vomiting, decreased weight, decreased calcium, decreased glucose, prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time, and alopecia.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER). Female Breast Cancer. [cited 2020 Jun 2]. Available from: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html
-
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Breast Cancer in Men. [cited 2020 Jun 2]. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer-in-men/about/key-statistics....
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Guidelines. Breast Cancer [about 4 screens]. [cited 2020 June 2]. Available from https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx.
-
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program (SEER). Female Breast Cancer Subtypes. [cited 2020 Jun 2]. Available from: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous