Stac protein regulates release of neuropeptides
- PMID: 33168737
- PMCID: PMC7703553
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2009224117
Stac protein regulates release of neuropeptides
Abstract
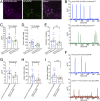
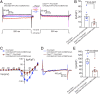
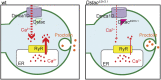
Neuropeptides are important for regulating numerous neural functions and behaviors. Release of neuropeptides requires long-lasting, high levels of cytosolic Ca2+ However, the molecular regulation of neuropeptide release remains to be clarified. Recently, Stac3 was identified as a key regulator of L-type Ca2+ channels (CaChs) and excitation-contraction coupling in vertebrate skeletal muscles. There is a small family of stac genes in vertebrates with other members expressed by subsets of neurons in the central nervous system. The function of neural Stac proteins, however, is poorly understood. Drosophila melanogaster contain a single stac gene, Dstac, which is expressed by muscles and a subset of neurons, including neuropeptide-expressing motor neurons. Here, genetic manipulations, coupled with immunolabeling, Ca2+ imaging, electrophysiology, and behavioral analysis, revealed that Dstac regulates L-type CaChs (Dmca1D) in Drosophila motor neurons and this, in turn, controls the release of neuropeptides.
Keywords: Drosophila melanogaster; L-type voltage-gated calcium channel; neuropeptide; stac.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
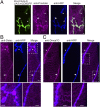
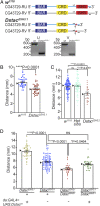
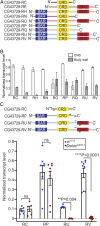
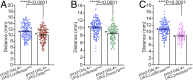

References
-
- Donaldson Z. R., Young L. J., Oxytocin, vasopressin, and the neurogenetics of sociality. Science 322, 900–904 (2008). - PubMed
-
- García A. G., García-De-Diego A. M., Gandía L., Borges R., García-Sancho J., Calcium signaling and exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Physiol. Rev. 86, 1093–1131 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Inoue M., et al. , Homogeneous Ca2+ stores in rat adrenal chromaffin cells. Cell Calcium 33, 19–26 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Morris J. F., Pow D. V., Widespread release of peptides in the central nervous system: Quantitation of tannic acid-captured exocytoses. Anat. Rec. 231, 437–445 (1991). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

