Characterization of p190-Bcr-Abl chronic myeloid leukemia reveals specific signaling pathways and therapeutic targets
- PMID: 33168949
- PMCID: PMC8257498
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-020-01082-4
Characterization of p190-Bcr-Abl chronic myeloid leukemia reveals specific signaling pathways and therapeutic targets
Abstract
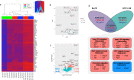
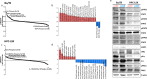
The oncogenic protein Bcr-Abl has two major isoforms, p190Bcr-Abl and p210Bcr-Abl. While p210Bcr-Abl is the hallmark of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), p190Bcr-Abl occurs in the majority of Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph + ALL) patients. In CML, p190Bcr-Abl occurs in a minority of patients associating with distinct hematological features and inferior outcomes, yet the pathogenic role of p190Bcr-Abl and potential targeting therapies are largely uncharacterized. We employed next generation sequencing, phospho-proteomic profiling, and drug sensitivity testing to characterize p190Bcr-Abl in CML and hematopoietic progenitor cell line models (Ba/f3 and HPC-LSK). p190Bcr-Abl CML patients demonstrated poor response to imatinib and frequent mutations in epigenetic modifiers genes. In contrast with p210Bcr-Abl, p190Bcr-Abl exhibited specific transcriptional upregulation of interferon, interleukin-1 receptor, and P53 signaling pathways, associated with hyperphosphorylation of relevant signaling molecules including JAK1/STAT1 and PAK1 in addition to Src hyperphosphorylation. Comparable to p190Bcr-Abl CML patients, p190Bcr-Abl cell lines demonstrated similar transcriptional and phospho-signaling signatures. With the drug sensitivity screening we identified targeted drugs with specific activity in p190Bcr-Abl cell lines including IAP-, PAK1-, and Src inhibitors and glucocorticoids. Our results provide novel insights into the mechanisms underlying the distinct features of p190Bcr-Abl CML and promising therapeutic targets for this high-risk patient group.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by Academy of Finland (grant no. 292605 and 287224), the Finnish Funding Agency for Innovation (Dnro 6113/31/2016), Finnish special governmental subsidy for health sciences, research and training, Signe and Ane Gyllenberg Foundation, Finnish Cultural Foundation, Ida Montin Foundation, Nordic Cancer Union, Helsinki Institute of Life Science, Cancer Foundation Finland, Relander Foundation, Incyte Nordic Hematology grant, and Finnish Cancer Institute. SM has received honoraria and research funding from Novartis, Pfizer, and Bristol-Myers Squibb (not related to this study). SAA and HH have received research funding from Incyte.
Figures



References
-
- Pane F, Intrieri M, Quintarelli C, Izzo B, Muccioli GC, Salvatore F. BCR/ABL genes and leukemic phenotype: from molecular mechanisms to clinical correlations. Oncogene. 2002;21:8652–67. - PubMed
-
- Wong S, Witte ON. The BCR-ABL story: bench to bedside and back. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:247–306. - PubMed
-
- Demehri S, O’Hare T, Eide CA, Smith CA, Tyner JW, Druker BJ, et al. The function of the pleckstrin homology domain in BCR–ABL-mediated leukemogenesis. Leukemia. 2010;24:226–9. - PubMed
-
- Roumiantsev S, de Aos IE, Varticovski L, Ilaria RL, Van, Etten RA. The src homology 2 domain of Bcr/Abl is required for efficient induction of chronic myeloid leukemia-like disease in mice but not for lymphoid leukemogenesis or activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Blood. 2001;97:4–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

