Protein higher-order-structure determination by fast photochemical oxidation of proteins and mass spectrometry analysis
- PMID: 33169002
- PMCID: PMC10476649
- DOI: 10.1038/s41596-020-0396-3
Protein higher-order-structure determination by fast photochemical oxidation of proteins and mass spectrometry analysis
Abstract
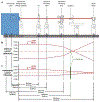
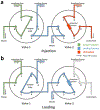
The higher-order structure (HOS) of proteins plays a critical role in their function; therefore, it is important to our understanding of their function that we have as much information as possible about their three-dimensional structure and how it changes with time. Mass spectrometry (MS) has become an important tool for determining protein HOS owing to its high throughput, mid-to-high spatial resolution, low sample amount requirement and broad compatibility with various protein systems. Modern MS-based protein HOS analysis relies, in part, on footprinting, where a reagent reacts 'to mark' the solvent-accessible surface of the protein, and MS-enabled proteomic analysis locates the modifications to afford a footprint. Fast photochemical oxidation of proteins (FPOP), first introduced in 2005, has become a powerful approach for protein footprinting. Laser-induced hydrogen peroxide photolysis generates hydroxyl radicals that react with solvent-accessible side chains (14 out of 20 amino acid side chains) to fulfill the footprinting. The reaction takes place at sub-milliseconds, faster than most of labeling-induced protein conformational changes, thus enabling a 'snapshot' of protein HOS in solution. As a result, FPOP has been employed in solving several important problems, including mapping epitopes, following protein aggregation, locating small molecule binding, measuring ligand-binding affinity, monitoring protein folding and unfolding and determining hidden conformational changes invisible to other methods. Broader adoption will be promoted by dissemination of the technical details for assembling the FPOP platform and for dealing with the complexities of analyzing FPOP data. In this protocol, we describe the FPOP platform, the conditions for successful footprinting and its examination by mass measurements of the intact protein, the post-labeling sample handling and digestion, the liquid chromatography-tandem MS analysis of the digested sample and the data analysis with Protein Metrics Suite. This protocol is intended not only as a guide for investigators trying to establish an FPOP platform in their own lab but also for those willing to incorporate FPOP as an additional tool in addressing their questions of interest.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare an ongoing collaboration with Protein Metrics in establishing an HDX data processing platform, a topic that is not related to this protocol. The recommendation of using Protein Metrics as preferred data processing software for FPOP data predates the ongoing collaboration.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

