Characterization of Chemically Activated Pyrolytic Carbon Black Derived from Waste Tires as a Candidate for Nanomaterial Precursor
- PMID: 33172181
- PMCID: PMC7694789
- DOI: 10.3390/nano10112213
Characterization of Chemically Activated Pyrolytic Carbon Black Derived from Waste Tires as a Candidate for Nanomaterial Precursor
Abstract
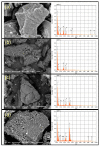
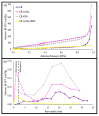
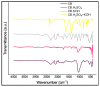
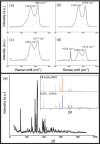
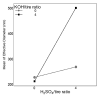
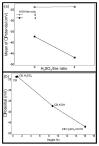
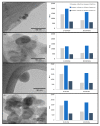
Pyrolysis is a feasible solution for environmental problems related to the inadequate disposal of waste tires, as it leads to the recovery of pyrolytic products such as carbon black, liquid fuels and gases. The characteristics of pyrolytic carbon black can be enhanced through chemical activation in order to produce the required properties for its application. In the search to make the waste tire pyrolysis process profitable, new applications of the pyrolytic solid products have been explored, such as for the fabrication of energy-storage devices and precursor in the synthesis of nanomaterials. In this study, waste tires powder was chemically activated using acid (H2SO4) and/or alkali (KOH) to recover pyrolytic carbon black with different characteristics. H2SO4 removed surface impurities more thoroughly, improving the carbon black's surface area, while KOH increased its oxygen content, which improved the carbon black's stability in water suspension. Pyrolytic carbon black was fully characterized by elemental analysis, inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption/desorption, scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), dynamic light scattering (DLS), and ζ potential measurement. In addition, the pyrolytic carbon black was used to explore its feasibility as a precursor for the synthesis of carbon dots; synthesized carbon dots were analyzed preliminarily by SEM and with a fluorescence microplate reader, revealing differences in their morphology and fluorescence intensity. The results presented in this study demonstrate the effect of the activating agent on pyrolytic carbon black from waste tires and provide evidence of the feasibility of using waste tires for the synthesis of nanomaterials such as carbon dots.
Keywords: carbon dots; chemical activation; particle characterization; pyrolysis; valorization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Production and Upgrading of Recovered Carbon Black from the Pyrolysis of End-of-Life Tires.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 9;15(6):2030. doi: 10.3390/ma15062030. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35329479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, Purification, and Characterization of Carbon Dots from Non-Activated and Activated Pyrolytic Carbon Black.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jan 18;12(3):298. doi: 10.3390/nano12030298. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159643 Free PMC article.
-
Upgrading pyrolytic residue from waste tires to commercial carbon black.Waste Manag Res. 2018 May;36(5):436-444. doi: 10.1177/0734242X18764292. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Waste Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 29589516
-
Upgrading recovered carbon black (rCB) from industrial-scale end-of-life tires (ELTs) pyrolysis to activated carbons: Material characterization and CO2 capture abilities.Environ Res. 2024 Apr 15;247:118169. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.118169. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38244973
-
Waste tire pyrolysis and desulfurization of tire pyrolytic oil (TPO) - A review.J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2023 Mar;73(3):159-177. doi: 10.1080/10962247.2022.2136781. Epub 2023 Jan 11. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36269581 Review.
Cited by
-
Adsorption of heavy metal onto biomass-derived activated carbon: review.RSC Adv. 2023 Jan 31;13(7):4275-4302. doi: 10.1039/d2ra07911a. eCollection 2023 Jan 31. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 36760304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chitosan-Based Carbon Dots with Applied Aspects: New Frontiers of International Interest in a Material of Marine Origin.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 16;20(12):782. doi: 10.3390/md20120782. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36547929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tailoring a hierarchical porous carbon electrode from carbon black via 3D diatomite morphology control for enhanced electrochemical performance.Nanoscale Adv. 2024 Sep 25;6(24):6265-77. doi: 10.1039/d4na00680a. Online ahead of print. Nanoscale Adv. 2024. PMID: 39430303 Free PMC article.
-
Production and Upgrading of Recovered Carbon Black from the Pyrolysis of End-of-Life Tires.Materials (Basel). 2022 Mar 9;15(6):2030. doi: 10.3390/ma15062030. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35329479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing the production of PHA in Scenedesmus sp. by the addition of green synthesized nitrogen, phosphorus, and nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon dots.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Jun 4;17(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02522-4. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 38835059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayoob A.K., Fadhil A.B. Valorization of waste tires in the synthesis of an effective carbon based catalyst for biodiesel production from a mixture of non-edible oils. Fuel. 2020;264:116754. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116754. - DOI
-
- Kirchherr J., Reike D., Hekkert M. Conceptualizing the circular economy: An analysis of 114 definitions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017;127:221–232. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.005. - DOI
-
- Peronard J.P., Ballantyne A.G. Broadening the understanding of the role of consumer services in the circular economy: Toward a conceptualization of value creation processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019;239:118010. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118010. - DOI
-
- Taleb D.A., Hamid H.A., Deris R.R.R., Zulkifli M., Khalil N.A., Ahmad Yahaya A.N. Insights into pyrolysis of waste tire in fixed bed reactor: Thermal behavior. Mater. Today Proc. 2020:1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.569. - DOI
-
- Martínez J.D., Puy N., Murillo R., García T., Navarro M.V., Mastral A.M. Waste tyre pyrolysis—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013;23:179–213. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.02.038. - DOI

