HPV sensitizes OPSCC cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting autophagy through E7-mediated degradation of AMBRA1
- PMID: 33172332
- PMCID: PMC8526016
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1847444
HPV sensitizes OPSCC cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting autophagy through E7-mediated degradation of AMBRA1
Abstract
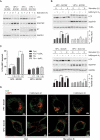
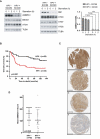
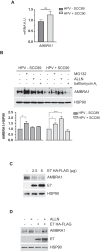
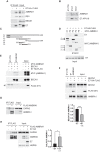
Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC) is an increasing world health problem with a more favorable prognosis for patients with human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive tumors compared to those with HPV-negative OPSCC. How HPV confers a less aggressive phenotype, however, remains undefined. We demonstrated that HPV-positive OPSCC cells display reduced macroautophagy/autophagy activity, mediated by the ability of HPV-E7 to interact with AMBRA1, to compete with its binding to BECN1 and to trigger its calpain-dependent degradation. Moreover, we have shown that AMBRA1 downregulation and pharmacological inhibition of autophagy sensitized HPV-negative OPSCC cells to the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin. Importantly, semi-quantitative immunohistochemical analysis in primary OPSCCs confirmed that AMBRA1 expression is reduced in HPV-positive compared to HPV-negative tumors. Collectively, these data identify AMBRA1 as a key target of HPV to impair autophagy and propose the targeting of autophagy as a viable therapeutic strategy to improve treatment response of HPV-negative OPSCC.Abbreviations: AMBRA1: autophagy and beclin 1 regulator 1; CDDP: cisplatin (CDDP); FFPE: formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE); HNC: head and neck cancers (HNC); HPV: human papillomavirus (HPV); hrHPV: high risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV); OCSCC: oral cavity squamous carcinomas (OCSSC); OPSCC: oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC); OS: overall survival (OS); qPCR: quantitative polymerase chain reaction; RB1: RB transcriptional corepressor 1; ROC: receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC).
Keywords: AMBRA1; autophagy; calpains; hpv-E7; oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Rob Ellis, Dr Marie Labus and Prof. Penny Lovat are directors of AMLo Biosciences Ltd. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, et al. The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual: continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin [Internet] 2017. [cited 2019 Apr 4]; 67(2):93–99. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28094848 - PubMed
-
- IARC working group on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Biological agents. Volume 100 B. A review of human carcinogens. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum [Internet] 2012. [cited 2019 Aug 5]; 100:1–441. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23189750 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schiffman M, Doorbar J, Wentzensen N, et al. Carcinogenic human papillomavirus infection. Nat Rev Dis Prim. [Internet] 2016. [cited 2019 Jul 23]; 2:16086. Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/nrdp201686 - PubMed
-
- Darnell GA, Schroder WA, Antalis TM, et al. Human Papillomavirus E7 requires the protease calpain to degrade the retinoblastoma protein. J Biol Chem [Internet] 2007. [cited 2019 Apr 4]; 282(52):37492–37500. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17977825 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
