Laser Capture Microdissection-Based RNA Microsequencing Reveals Optic Nerve Crush-Related Early mRNA Alterations in Retinal Ganglion Cell Layer
- PMID: 33173609
- PMCID: PMC7594581
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.11.30
Laser Capture Microdissection-Based RNA Microsequencing Reveals Optic Nerve Crush-Related Early mRNA Alterations in Retinal Ganglion Cell Layer
Abstract
Purpose: To establish a method of laser capture microdissection (LCM) and RNA microsequencing for exploring optic nerve crush (ONC)-related early mRNA alterations in retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer.
Methods: An LCM protocol was developed using retinal tissue sections to obtain high-quality RNA for microsequencing. Cells in the RGC layer were collected by laser pressure catapulting (LPC) using a PALM Zeiss UV LCM system. The effect of section thickness and slide type on tissue capture success and RNA yield and the integrity after LCM were evaluated. The optimal LCM protocol was used to explore ONC-related early mRNA alterations in the RGC layer. Candidate genes were validated by real-time polymerase chain reaction of the RGC layer tissue dissected by "cut and LPC" using the same LCM system.
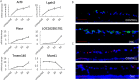
Results: We successfully established an optimal LCM protocol using 30-µm-thick retinal tissue sections mounted on glass slides and laser pressure catapulting (LPC) to collect cells in the RGC layer and to obtain high-quality RNA for microsequencing. On the basis of our protocol, we identified 8744 differentially expressed genes that were involved in ONC-related early mRNA alterations in the RGC layer. Candidate genes included Atf3, Lgals3, LOC102551701, Plaur, Tmem140, and Maml1.
Conclusions: The LCM-based single-cell RNA sequencing allowed a new sight into the early mRNA changes of RGCs highlighting new molecules associated to ONC.
Translational relevance: This technique will be helpful for more accurate transcriptome analysis of clinical pathological samples of ophthalmology and provide important reference for the discovery of new pathological diagnosis indicators and drug development targets.
Keywords: laser capture microdissection; microsequencing; optic nerve crush; retinal ganglion cell layer.
Copyright 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: D. Pan, None; M. Xu, None; X. Chang, None; M. Xia, None; Y. Fang, None; Y. Fu, None; W. Shen, None; Y. Wang, None; X. Sun, None
Figures



Similar articles
-
LCM-Seq for Retinal Cell Layer-Specific Responses During Optic Nerve Regeneration.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2636:311-321. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3012-9_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36881308
-
Early Gene Expression Profile in Retinal Ganglion Cell Layer After Optic Nerve Crush in Mice.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Jan 1;59(1):370-380. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22438. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29346801
-
Activation of the BMP4/Smad1 Pathway Promotes Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Apr 1;60(5):1748-1759. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-26449. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31022296
-
Profiling cell-type specific gene expression in post-mortem human brain samples through laser capture microdissection.Methods. 2022 Nov;207:3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2022.08.013. Epub 2022 Sep 3. Methods. 2022. PMID: 36064002 Review.
-
Laser Capture Proteomics: spatial tissue molecular profiling from the bench to personalized medicine.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021 Oct;18(10):845-861. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2021.1984886. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34607525 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Immunohistochemical Biomarkers in Diabetic Wistar Rats with Periodontal Disease.J Pers Med. 2024 May 15;14(5):527. doi: 10.3390/jpm14050527. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38793109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen M, Xiang Z, Cai J. The anti-apoptotic and neuro-protective effects of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells (hUCB-MSCs) on acute optic nerve injury is transient. Brain Res. 2013; 1532: 63–75. - PubMed
-
- Garrido-Gil P, Fernandez-Rodriguez P, Rodriguez-Pallares J, Labandeira-Garcia JL. Laser capture microdissection protocol for gene expression analysis in the brain. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017; 148(3): 299–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

