Heterochirality and Halogenation Control Phe-Phe Hierarchical Assembly
- PMID: 33175503
- PMCID: PMC7872421
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c06041
Heterochirality and Halogenation Control Phe-Phe Hierarchical Assembly
Abstract
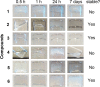
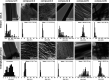
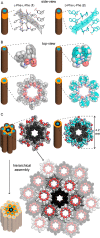
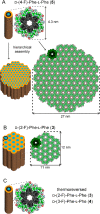
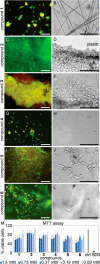
Diphenylalanine is an amyloidogenic building block that can form a versatile array of supramolecular materials. Its shortcomings, however, include the uncontrolled hierarchical assembly into microtubes of heterogeneous size distribution and well-known cytotoxicity. This study rationalized heterochirality as a successful strategy to address both of these pitfalls and it provided an unprotected heterochiral dipeptide that self-organized into a homogeneous and optically clear hydrogel with excellent ability to sustain fibroblast cell proliferation and viability. Substitution of one l-amino acid with its d-enantiomer preserved the ability of the dipeptide to self-organize into nanotubes, as shown by single-crystal XRD analysis, whereby the pattern of electrostatic and hydrogen bonding interactions of the backbone was unaltered. The effect of heterochirality was manifested in subtle changes in the positioning of the aromatic side chains, which resulted in weaker intermolecular interactions between nanotubes. As a result, d-Phe-l-Phe self-organized into homogeneous nanofibrils with a diameter of 4 nm, corresponding to two layers of peptides around a water channel, and yielded a transparent hydrogel. In contrast with homochiral Phe-Phe stereoisomer, it formed stable hydrogels thermoreversibly. d-Phe-l-Phe displayed no amyloid toxicity in cell cultures with fibroblast cells proliferating in high numbers and viability on this biomaterial, marking it as a preferred substrate over tissue-culture plastic. Halogenation also enabled the tailoring of d-Phe-l-Phe self-organization. Fluorination allowed analogous supramolecular packing as confirmed by XRD, thus nanotube formation, and gave intermediate levels of bundling. In contrast, iodination was the most effective strategy to augment the stability of the resulting hydrogel, although at the expense of optical transparency and biocompatibility. Interestingly, iodine presence hindered the supramolecular packing into nanotubes, resulting instead into amphipathic layers of stacked peptides without the occurrence of halogen bonding. By unravelling fine details to control these materials at the meso- and macro-scale, this study significantly advanced our understanding of these systems.
Keywords: chirality; d-amino acids; halogenation; hydrogels; peptides; phenylalanine; self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Heterochirality Restricts the Self-Assembly of Phenylalanine Dipeptides Capped with Highly Aromatic Groups.J Phys Chem B. 2020 Jul 16;124(28):5913-5918. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.0c04513. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Phys Chem B. 2020. PMID: 32559085
-
Identification of heterochirality-mediated stereochemical interactions in peptide architectures.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023 Apr;224:113200. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113200. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023. PMID: 36774824
-
Dipeptide self-assembly into water-channels and gel biomaterial.Org Biomol Chem. 2022 Aug 10;20(31):6211-6218. doi: 10.1039/d2ob00622g. Org Biomol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35575102
-
Tripeptides Featuring Dehydrophenylalanine and Homophenylalanine: Homo- Versus Hetero-Chirality and Sequence Effects on Self-Assembly and Gelation.Gels. 2025 Feb 24;11(3):164. doi: 10.3390/gels11030164. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40136869 Free PMC article.
-
Phe-Phe-Based Macroscopic Supramolecular Hydrogel Construction Strategies and Biomedical Applications.Chem Bio Eng. 2024 Aug 12;1(8):664-677. doi: 10.1021/cbe.4c00110. eCollection 2024 Sep 26. Chem Bio Eng. 2024. PMID: 39974324 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amyloids as Building Blocks for Macroscopic Functional Materials: Designs, Applications and Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10698. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910698. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion Channels and Transporters as Therapeutic Agents: From Biomolecules to Supramolecular Medicinal Chemistry.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 12;10(4):885. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040885. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short Peptides for Hydrolase Supramolecular Mimicry and Their Potential Applications.Gels. 2023 Aug 23;9(9):678. doi: 10.3390/gels9090678. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37754360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Assessment of Chirality of Protein Secondary Structures and Phenylalanine Peptide Nanotubes.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Dec 5;11(12):3299. doi: 10.3390/nano11123299. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34947648 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Assembly of Unprotected Dipeptides into Hydrogels: Water-Channels Make the Difference.Chembiochem. 2022 Jan 19;23(2):e202100518. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100518. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 34784433 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

