The multifaceted functions of follicular regulatory T cells
- PMID: 33176227
- PMCID: PMC7744352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.10.009
The multifaceted functions of follicular regulatory T cells
Abstract
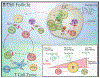
The immune system is capable of generating robust antibody responses to foreign antigens during infection and vaccination, while simultaneously limiting antibodies to self-antigens. T follicular regulatory (Tfr) cells are a subset of follicular T cell with specialized roles in regulating humoral immunity. Although Tfr cells have been studied for the past 10 years, their roles have remained elusive. In this review we discuss the current understanding of Tfr cell functions in autoimmunity and how Tfr cells simultaneously control foreign and autoantigen specific antibody responses. We highlight new tools that enable in-depth study of Tfr cells in vivo and recent data suggesting an important role for Tfr cells in limiting participation of autoreactive B cells in germinal centers.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Conflict
Arlene Sharpe and Peter Sage do not have conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

