Morphological and pathological changes of Eustachian tube mucosa in an animal model of eosinophilic otitis media
- PMID: 33176987
- PMCID: PMC9483936
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.09.011
Morphological and pathological changes of Eustachian tube mucosa in an animal model of eosinophilic otitis media
Abstract
Introduction: Eosinophilic otitis media is an intractable otitis media and a fairly common middle ear disease. However, the pathogenesis of eosinophilic otitis media is obscure.
Objective: To observe the pathological and ultrastructural changes of the Eustachian tube mucosal epithelium in rats with eosinophilic otitis media and further explore the pathogenesis of eosinophilic otitis media.
Methods: Animals were intraperitoneally injected with 2000 mg ovalbumin and 100 mg aluminum hydroxide (alum) on day 0, followed by 100 mg ovalbumin and 100 mg alum injection on days 7 and 14. Next they were topically boosted by daily application of 100 mg ovalbumin solution via nasal drip and intratympanic injection of 0.1 mL ovalbumin (1000 mg/mL) in the right ear (group A, n = 80) and 0.1 mL saline in the left ear as control (group B, n = 80) starting on day 21 and continuing for 14 days. The temporal bones were dissected on the 35th, 38th, 41st and 43rd day separately under anesthesia. Scanning electron microscopy, hematoxylin-eosin and toluidine blue staining were used to observe the pathological and morphological changes of Eustachian tube mucosa stained samples. Moreover, inflammatory cells and cilia were counted.
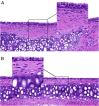
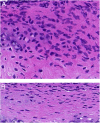
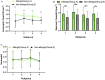
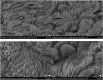
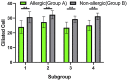
Results: The epithelium of the Eustachian tube in group A was swollen and thickened. The cilia were arranged in a disorderly manner and partially detached. Eosinophils infiltrated the submucosal layer of the Eustachian tube, and their number increased significantly compared with that in group B (p < 0.05). Simultaneously, mast cell degranulation was observed in group A. Scanning electron microscopy revealed that the cilia were lodged and gathered along the whole length of Eustachian tube in group A. Ciliated cell density was significantly lower than that in Group B (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: In the eosinophilic otitis media model, allergy caused significant changes in pathology and morphology of the Eustachian tube mucosa, affecting the normal function of the Eustachian tube which played an important role in the occurrence and development of eosinophilic otitis media.
Keywords: Allergy; Cilia; Eosinophilic otitis media; Eustachian tube; Mucosa.
Copyright © 2020 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Observation of mucosa of eustachian tube with scanning electron microscope on spontaneous otitis media in mice].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Jul;29(14):1299-301. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26672248 Chinese.
-
Clinical characteristics of so called eosinophilic otitis media.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2002 Jan;29(1):19-28. doi: 10.1016/s0385-8146(01)00124-9. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2002. PMID: 11772486
-
[Histopathological and ultracytochemical observation of mucosa on the eustachian tube and middle ear with experimental secretory otitis media].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2003 Jun;17(6):359-61. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14503375 Chinese.
-
Otitis media and eustachian tube dysfunction: connection to allergic rhinitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997 Feb;99(2):S787-97. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70130-1. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9042072 Review.
-
Role of allergy in eustachian tube blockage and otitis media with effusion: a review.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996 Apr;114(4):562-8. doi: 10.1016/S0194-59989670247-4. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1996. PMID: 8643265 Review.
Cited by
-
Is Allergic Rhinitis Related to Otitis Media with Effusion in Adults and Children? Applying Epidemiological Guidelines for Causation.Cells. 2025 May 30;14(11):805. doi: 10.3390/cells14110805. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40497981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcutaneous Injection and Brush Application of Ovalbumin-Aluminum Salt Solution Induces Dermatitis-like Changes in Mice.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 3;14(5):1701. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051701. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40095628 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of the cognition-related pathogenic proteins in plasma neuronal-derived exosomes among normal cognitive adults over 45 years old with olfactory dysfunction.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Jul;279(7):3467-3476. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07143-3. Epub 2021 Oct 24. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34693486
References
-
- Martines F., Bentivegna D., Di Piazza F., Martinciglio G., Sciacca V., Martines E. The point prevalence of otitis media with effusion among primary school children in Western Sicily. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267:709–714. - PubMed
-
- Zielhuis G.A., Straatman H., Rach G.H., van den Broek P. Analysis and presentation of data on the natural course of otitis media with effusion in children. Int J Epidemiol. 1990;19:1037–1044. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen L.H., Manoukian J.J., Tewfik T.L., Sobol S.E., Joubert P., Mazer B.D., et al. Evidence of allergic inflammation in the middle ear and nasopharynx in atopic children with otitis media with effusion. J Otolaryngol. 2004;33:345–351. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen L.H., Manoukian J.J., Sobol S.E., Tewfik T.L., Mazer B.D., Schloss M.D., et al. Similar allergic inflammation in the middle ear and the upper airway: evidence linking otitis media with effusion to the united airways concept. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:1110–1115. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

