Risk Factors for CKD Progression: Overview of Findings from the CRIC Study
- PMID: 33177074
- PMCID: PMC8092061
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07830520
Risk Factors for CKD Progression: Overview of Findings from the CRIC Study
Abstract
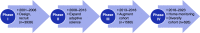
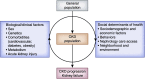
The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study is an ongoing, multicenter, longitudinal study of nearly 5500 adults with CKD in the United States. Over the past 10 years, the CRIC Study has made significant contributions to the understanding of factors associated with CKD progression. This review summarizes findings from longitudinal studies evaluating risk factors associated with CKD progression in the CRIC Study, grouped into the following six thematic categories: (1) sociodemographic and economic (sex, race/ethnicity, and nephrology care); (2) behavioral (healthy lifestyle, diet, and sleep); (3) genetic (apoL1, genome-wide association study, and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system pathway genes); (4) cardiovascular (atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and vascular stiffness); (5) metabolic (fibroblast growth factor 23 and urinary oxalate); and (6) novel factors (AKI and biomarkers of kidney injury). Additionally, we highlight areas where future research is needed, and opportunities for interdisciplinary collaboration.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; progression of chronic renal failure; risk factors.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Kidney disease statistics for the United States. Available at: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/kidney-di.... Accessed August 9, 2017
-
- Lash JP, Go AS, Appel LJ, He J, Ojo A, Rahman M, Townsend RR, Xie D, Cifelli D, Cohan J, Fink JC, Fischer MJ, Gadegbeku C, Hamm LL, Kusek JW, Landis JR, Narva A, Robinson N, Teal V, Feldman HI; Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study Group: Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study: Baseline characteristics and associations with kidney function [published correction appears in Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6: 2548–2553, 2011]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4: 1302–1311, 2009. 10.2215/CJN.00070109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feldman HI, Appel LJ, Chertow GM, Cifelli D, Cizman B, Daugirdas J, Fink JC, Franklin-Becker ED, Go AS, Hamm LL, He J, Hostetter T, Hsu CY, Jamerson K, Joffe M, Kusek JW, Landis JR, Lash JP, Miller ER, Mohler ER 3rd, Muntner P, Ojo AO, Rahman M, Townsend RR, Wright JT; Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study Investigators: The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) study: Design and methods. J Am Soc Nephrol 14[Suppl 2]: S148–S153, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Denker M, Boyle S, Anderson AH, Appel LJ, Chen J, Fink JC, Flack J, Go AS, Horwitz E, Hsu CY, Kusek JW, Lash JP, Navaneethan S, Ojo AO, Rahman M, Steigerwalt SP, Townsend RR, Feldman HI; Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study Investigators: Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort study (CRIC): Overview and summary of selected findings. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10: 2073–2083, 2015. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072231/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002548/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM109036/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060963/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060980/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119199/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000003/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK120811/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061028/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK092290/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061021/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL134634/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK118736/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060990/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061022/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK114857/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029879/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

