Amyloid-like oligomerization of AIMP2 contributes to α-synuclein interaction and Lewy-like inclusion
- PMID: 33177178
- PMCID: PMC8082540
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax0091
Amyloid-like oligomerization of AIMP2 contributes to α-synuclein interaction and Lewy-like inclusion
Abstract
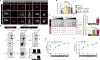
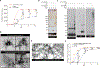
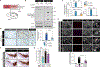
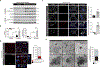
Lewy bodies are pathological protein inclusions present in the brain of patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). These inclusions consist mainly of α-synuclein with associated proteins, such as parkin and its substrate aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase complex-interacting multifunctional protein-2 (AIMP2). Although AIMP2 has been suggested to be toxic to dopamine neurons, its roles in α-synuclein aggregation and PD pathogenesis are largely unknown. Here, we found that AIMP2 exhibits a self-aggregating property. The AIMP2 aggregate serves as a seed to increase α-synuclein aggregation via specific and direct binding to the α-synuclein monomer. The coexpression of AIMP2 and α-synuclein in cell cultures and in vivo resulted in the rapid formation of α-synuclein aggregates with a corresponding increase in toxicity. Moreover, accumulated AIMP2 in mouse brain was largely redistributed to insoluble fractions, correlating with the α-synuclein pathology. Last, we found that α-synuclein preformed fibril (PFF) seeding, adult Parkin deletion, or oxidative stress triggered a redistribution of both AIMP2 and α-synuclein into insoluble fraction in cells and in vivo. Supporting the pathogenic role of AIMP2, AIMP2 knockdown ameliorated the α-synuclein aggregation and dopaminergic cell death in response to PFF or 6-hydroxydopamine treatment. Together, our results suggest that AIMP2 plays a pathological role in the aggregation of α-synuclein in mice. Because AIMP2 insolubility and coaggregation with α-synuclein have been seen in the PD Lewy body, targeting pathologic AIMP2 aggregation might be useful as a therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative α-synucleinopathies.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures



Similar articles
-
AIMP2 accumulation in brain leads to cognitive deficits and blood secretion in Parkinson's disease.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 10;22(1):919. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05666-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39390613 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of AIMP2 aggregation attenuates α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in Parkinson's disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Dec;156:113908. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113908. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36283223
-
Lewy body-associated proteins: victims, instigators, or innocent bystanders? The case of AIMP2 and alpha-synuclein.Neurobiol Dis. 2021 Aug;156:105417. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105417. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Neurobiol Dis. 2021. PMID: 34102275 Review.
-
14-3-3 Proteins Reduce Cell-to-Cell Transfer and Propagation of Pathogenic α-Synuclein.J Neurosci. 2018 Sep 19;38(38):8211-8232. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1134-18.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30093536 Free PMC article.
-
How can rAAV-α-synuclein and the fibril α-synuclein models advance our understanding of Parkinson's disease?J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):131-155. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13627. Epub 2016 May 4. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27018978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AIMP2 accumulation in brain leads to cognitive deficits and blood secretion in Parkinson's disease.J Transl Med. 2024 Oct 10;22(1):919. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05666-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39390613 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase interacting multifunctional protein-2 and α-synuclein by steroid derivative is neuroprotective in Parkinson's model.iScience. 2024 Oct 11;27(11):111165. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111165. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39569370 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation and conformational strains of α-Synuclein: implications for Parkinson's disease pathogenesis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Oct 23;17:1494218. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1494218. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39507104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dual Role of Survival Genes in Neurons and Cancer Cells: a Strategic Clinical Application of DX2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cancer.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025 Jan 1;33(1):75-85. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.138. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2025. PMID: 39711064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Biology of Parkin: Clues to the Development of New Therapeutics for Parkinson's Disease.CNS Drugs. 2022 Dec;36(12):1249-1267. doi: 10.1007/s40263-022-00973-7. Epub 2022 Nov 15. CNS Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36378485 Review.
References
-
- Spillantini MG, Goedert M, The alpha-synucleinopathies: Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920, 16–27 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Lang AE, Lozano AM, Parkinson’s disease. Second of two parts. N Engl J Med 339, 1130–1143 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Lang AE, Lozano AM, Parkinson’s disease. First of two parts. N Engl J Med 339, 1044–1053 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Norris EH, Giasson BI, Lee VM, Alpha-synuclein: normal function and role in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Top Dev Biol 60, 17–54 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

