COVID-19 Outbreak: Pathogenesis, Current Therapies, and Potentials for Future Management
- PMID: 33178016
- PMCID: PMC7596415
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.563478
COVID-19 Outbreak: Pathogenesis, Current Therapies, and Potentials for Future Management
Abstract
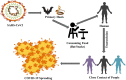
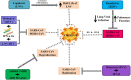
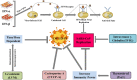
At the end of 2019, a novel coronavirus (CoV) was found at the seafood market of Hubei province in Wuhan, China, and this virus was officially named coronavirus diseases 2019 (COVID-19) by World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19 is mainly characterized by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV2) and creates public health concerns as well as significant threats to the economy around the world. Unfortunately, the pathogenesis of COVID-19 is unclear and there is no effective treatment of this newly life-threatening and devastating virus. Therefore, it is crucial to search for alternative methods that alleviate or inhibit the spread of COVID-19. In this review, we try to find out the etiology, epidemiology, symptoms as well as transmissions of this novel virus. We also summarize therapeutic interventions and suggest antiviral treatments, immune-enhancing candidates, general supplements, and CoV specific treatments that control replication and reproduction of SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Keywords: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; coronavirus; coronavirus disease 2019; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2; therapeutic interventions; transmission.
Copyright © 2020 Hossain, Hasana, Mamun, Uddin, Wahed, Sarker, Behl, Ullah, Begum, Bulbul, Amran, Rahman, Bin-Jumah, Alkahtani, Mousa, Aleya and Abdel-Daim.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

