Relationship Between the Fatty Acid Profiles and Gut Bacterial Communities of the Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) From Ecologically Different Habitats
- PMID: 33178151
- PMCID: PMC7593381
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.565267
Relationship Between the Fatty Acid Profiles and Gut Bacterial Communities of the Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) From Ecologically Different Habitats
Abstract
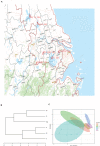
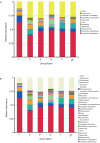
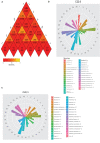
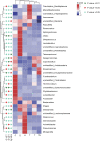
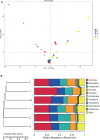
The gut microbiota plays an important role in a variety of physiological functions such as intestinal digestion, metabolic homeostasis, immune response, and responses to disease treatment. Whether there is a relationship between gut microbial communities and fatty acid (FA) profiles of Chinese mitten crab is unclear. Hence, we analyzed the relationship between FA profiles and the gut bacterial communities of six Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) populations from different lakes. The crabs were sampled from six different lakes in Jiangsu Province, China. The FA profiles of these crab populations were compared and clustered, and then used to determine the relationship between geographic location and FA composition. We also characterized the gut microbial communities of these crabs using 16S rRNA high-throughput gene sequencing. The FA profiles varied significantly (P < 0.05) between crabs from different geographical locations. A similar trend was also observed in the gut microbial communities, which also varied significantly based on their geographical origin (P < 0.05). Furthermore, alpha diversity, cluster analysis, and matching bacterial community structures with specific locations revealed patterns that significantly linked FA profiles to the gut microbiota. Further analysis of FA profiles and gut microbial community generated patterns that linked the two parameters. Hence, it was observed that the gut microbial community seems to contribute significantly to the FA composition of the Chinese mitten crab. However, further studies need to be conducted to investigate the interactions between gut microbial communities and the biochemical composition of the Chinese mitten crab, which will ultimately unravel the complexity of microbial ecosystems for potential applications in aquaculture and species conservation.
Keywords: Chinese mitten crab; fatty acid profiles; fatty acids and gut microbial interactions; geographic location; gut bacterial community.
Copyright © 2020 Su, Munganga, Du, Yu, Li, Yu, Wang, He, Li, Bouzoualegh, Xu and Tang.
Figures
References
-
- Allan G. J., Max T. L. (2010). Molecular genetic techniques and markers for ecological research. Nat. Educ. Knowledge 3:2.
-
- Antony M. M. (2016). Comparative evaluation of proximate composition of Etroplus suratensis from ecologically different areas of ashtamudi lake, Kerala. Int. J. Sci. Res. 5 959–965.
-
- Barłowska J., Pastuszka R., Rysiak A., Król J., Brodziak A., Kêdzierska-Matysek M., et al. (2018). Physicochemical and sensory properties of goat cheeses and their fatty acid profile in relation to the geographic region of production. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 71 699–708. 10.1111/1471-0307.12506 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

