Regulatory Mechanisms and Promising Applications of Quorum Sensing-Inhibiting Agents in Control of Bacterial Biofilm Formation
- PMID: 33178172
- PMCID: PMC7593269
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.589640
Regulatory Mechanisms and Promising Applications of Quorum Sensing-Inhibiting Agents in Control of Bacterial Biofilm Formation
Abstract
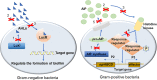
A biofilm is an assemblage of microbial cells attached to a surface and encapsulated in an extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) matrix. The formation of a biofilm is one of the important mechanisms of bacterial resistance, which not only leads to hard-to-control bacterial infections in humans and animals but also enables bacteria to be a major problem in various fields, such as food processing, wastewater treatment and metalworking. Quorum sensing (QS) is a bacterial cell-to-cell communication process that depends on the bacterial population density and is mediated by small diffusible signaling molecules called autoinducers (AIs). Bacteria use QS to regulate diverse arrays of functions, including virulence and biofilm formation. Therefore, the interference with QS by using QS inhibiting agents, including QS inhibitors (QSIs) and quorum quenching (QQ) enzymes, to reduce or even completely repress the biofilm formation of pathogenic bacteria appears to be a promising approach to control bacterial infections. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms of QS-regulating biofilm formation and QS-inhibiting agents that control bacterial biofilm formation, strategies for the discovery of new QS inhibiting agents, and the current applications of QS-inhibiting agents in several fields to provide insight into the development of effective drugs to control pathogenic bacteria.
Keywords: QS inhibitors; bacteria; biofilm formation; quorum quenching; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2020 Zhou, Zhang, Ge, Zhu and Pan.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

