The Novel Omega-6 Fatty Acid Docosapentaenoic Acid Positively Modulates Brain Innate Immune Response for Resolving Neuroinflammation at Early and Late Stages of Humanized APOE-Based Alzheimer's Disease Models
- PMID: 33178186
- PMCID: PMC7596305
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.558036
The Novel Omega-6 Fatty Acid Docosapentaenoic Acid Positively Modulates Brain Innate Immune Response for Resolving Neuroinflammation at Early and Late Stages of Humanized APOE-Based Alzheimer's Disease Models
Abstract
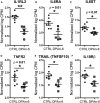
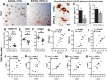
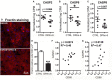
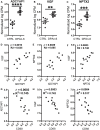
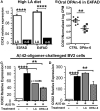
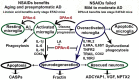
Neuroinflammation plays a crucial role in the development and progression of Alzheimer's disease (AD), in which activated microglia are found to be associated with neurodegeneration. However, there is limited evidence showing how neuroinflammation and activated microglia are directly linked to neurodegeneration in vivo. Besides, there are currently no effective anti-inflammatory drugs for AD. In this study, we report on an effective anti-inflammatory lipid, linoleic acid (LA) metabolite docosapentaenoic acid (DPAn-6) treatment of aged humanized EFAD mice with advanced AD pathology. We also report the associations of neuroinflammatory and/or activated microglial markers with neurodegeneration in vivo. First, we found that dietary LA reduced proinflammatory cytokines of IL1-β, IL-6, as well as mRNA expression of COX2 toward resolving neuroinflammation with an increase of IL-10 in adult AD models E3FAD and E4FAD mice. Brain fatty acid assays showed a five to six-fold increase in DPAn-6 by dietary LA, especially more in E4FAD mice, when compared to standard diet. Thus, we tested DPAn-6 in aged E4FAD mice. After DPAn-6 was administered to the E4FAD mice by oral gavage for three weeks, we found that DPAn-6 reduced microgliosis and mRNA expressions of inflammatory, microglial, and caspase markers. Further, DPAn-6 increased mRNA expressions of ADCYAP1, VGF, and neuronal pentraxin 2 in parallel, all of which were inversely correlated with inflammatory and microglial markers. Finally, both LA and DPAn-6 directly reduced mRNA expression of COX2 in amyloid-beta42 oligomer-challenged BV2 microglial cells. Together, these data indicated that DPAn-6 modulated neuroinflammatory responses toward resolution and improvement of neurodegeneration in the late stages of AD models.
Keywords: APOE; Alzheimer's disease; EFAD; docosapentaenoic acid; fatty acid; linoleic acid; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2020 Ma, Zhu, Morselli, Su, Pelligrini, Lu, Jones, Denver, Castro, Gu, Relampagos, Caoili, Teter, Frautschy and Cole.
Figures
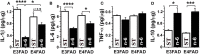

Similar articles
-
Human APOE4 increases microglia reactivity at Aβ plaques in a mouse model of Aβ deposition.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jun 19;11:111. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-111. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24948358 Free PMC article.
-
A small-molecule TLR4 antagonist reduced neuroinflammation in female E4FAD mice.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023 Oct 19;15(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01330-6. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37858252 Free PMC article.
-
APOE genotype-dependent pharmacogenetic responses to rapamycin for preventing Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jun;139:104834. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104834. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32173556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
25-Hydroxycholesterol amplifies microglial IL-1β production in an apoE isoform-dependent manner.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jun 17;17(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01869-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32552741 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Sphingolipids and Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 29;11:620348. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.620348. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33633739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-Specific Changes to Brain Fatty Acids, Plasmalogen, and Plasma Endocannabinoids in Offspring Exposed to Maternal and Postnatal High-Linoleic-Acid Diets.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 19;25(14):7911. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147911. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063152 Free PMC article.
-
Unsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Immunomodulatory Properties.Biology (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;12(2):279. doi: 10.3390/biology12020279. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Very-Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in the Central Nervous System and Their Potential Benefits for Treating Alcohol Use Disorder: Reviewing Pre-Clinical and Clinical Data.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 30;15(13):2993. doi: 10.3390/nu15132993. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dihydroxy-Metabolites of Dihomo-gamma-linolenic Acid Drive Ferroptosis-Mediated Neurodegeneration.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jan 10:2023.01.05.522933. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.05.522933. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Mar 16;9(5):870-882. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00052. PMID: 36711920 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Can the gut microbiome inform the effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation trials on cognition?Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2024 Mar 1;27(2):116-124. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000001007. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2024. PMID: 38170690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

