Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor Treatment as a Novel Therapy Attenuating Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 33178190
- PMCID: PMC7597449
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.564288
Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor Treatment as a Novel Therapy Attenuating Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
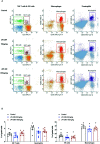
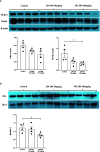
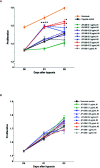
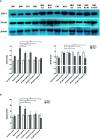
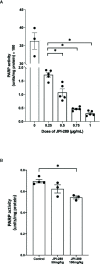
Intrarenal robust inflammatory response following ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a major factor in the pathogenesis of renal injury in ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI). Although numerous studies have investigated various agents of immune modulation or suppression for ischemic AKI, few showed reproducible effects. We hypothesized that poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor may favorably change post-ischemic intrarenal immunologic micromilieu by reducing damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) signals and improve renal outcome in ischemic AKI. The effects of JPI-289 (a PARP inhibitor) on early renal injury in a murine IRI model and hypoxic HK-2 cell model were investigated. Bilateral IRI surgery was performed in three groups of 9-week-old male C57BL/6 mice (control, JPI-289 50 mg/kg, and JPI-289 100 mg/kg; n = 9-10 in each group). Saline or JPI-289 was intraperitoneally injected. Renal function deterioration was significantly attenuated in the JPI-289 treatment groups in a dose-dependent manner. Inflammatory cell infiltration and proinflammatory cytokine/chemokine expressions in the post-ischemic kidneys were also attenuated by JPI-289 treatment. JPI-289 treatment at 0.5 and 0.75 μg/ml facilitated the proliferation of hypoxic HK-2 cells. PARP inhibition with JPI-289 treatment showed favorable effects in ischemic AKI by attenuating intrarenal inflammatory cascade in a murine model and facilitating proliferation of hypoxic HK-2 cells.
Keywords: Ischemia-reperfusion injury; acute kidney injury; inflammation; parthanatos; poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor; translational immunology.
Copyright © 2020 Jang, Lee, Jeon, Kim, Lee, Kwon, Kim, Kim, Ko and Huh.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor treatment on the repair process of ischemic acute kidney injury.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50630-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38167603 Free PMC article.
-
Early Treatment with Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 Inhibitor (JPI-289) Reduces Infarct Volume and Improves Long-Term Behavior in an Animal Model of Ischemic Stroke.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Sep;55(9):7153-7163. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0910-6. Epub 2018 Jan 30. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29383691
-
Neuroprotective effects of a novel poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor, JPI-289, in hypoxic rat cortical neurons.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017 Jun;44(6):671-679. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12757. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28370165
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-mediated cell injury in acute renal failure.Pharmacol Res. 2005 Jul;52(1):44-59. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2005.02.022. Pharmacol Res. 2005. PMID: 15911333 Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) and PARP Inhibitors: Mechanisms of Action and Role in Cardiovascular Disorders.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018 Dec;18(6):493-506. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9462-2. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29968072 Review.
Cited by
-
PARP-1-Associated Pathological Processes: Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 23;22(21):11441. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111441. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nephrotoxicity in cancer treatment: An update.Adv Cancer Res. 2022;155:77-129. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2022.03.005. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Adv Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35779877 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of DNA damage repair and precise targeted therapy in renal cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2022 Dec;48(6):213. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8428. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36263616 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in preventing neurodegenerative diseases.Fac Rev. 2021 Dec 1;10:81. doi: 10.12703/r/10-81. eCollection 2021. Fac Rev. 2021. PMID: 35028646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and its ambiguous role in cellular life and death.Cell Stress. 2023 Jan 23;7(1):1-6. doi: 10.15698/cst2023.01.275. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cell Stress. 2023. PMID: 36743979 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

