Use of T Cell Mediated Immune Functional Assays for Adjustment of Immunosuppressive or Anti-infective Agents in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33178194
- PMCID: PMC7593245
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.567715
Use of T Cell Mediated Immune Functional Assays for Adjustment of Immunosuppressive or Anti-infective Agents in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
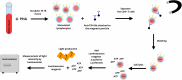
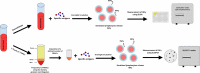
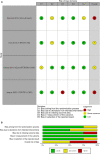
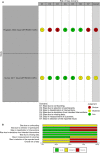
Background: Defining the optimal dosage of the immunosuppressive or duration of anti-infective agents is a challenge in solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients. We aimed to systematically review the literature regarding the use of T cell mediated immune functional assays (IFAs) for adjustment of the immunosuppressive or anti-infective agents in SOT recipients. Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Scopus, EMBASE, Web of Science (WOS), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and ClinicalTrials.gov to find human interventional studies or study protocols that used either in-house or commercially available IFAs for adjustment of the immunosuppressive or anti-infective agents in SOT recipients. Results: We included six clinical trials and six study protocols. Four out of the six clinical trials used interferon-γ release assays for cytomegalovirus (IGRA-CMV), and five out of the six registered study protocols planned to use IGRA-CMV for adjustment of anti-CMV antiviral (Valganciclovir) prophylaxis or preemptive therapy in SOT recipients. Primary or secondary anti-CMV prophylaxes were discontinued in SOT recipients who had positive IGRA-CMV results without an increase in the rate of CMV infection or reactivation. Among other IFAs, one clinical trial used interferon-γ release assays for tuberculosis (IGRA-TB), and one study used ImmuKnow for adjustment of the duration and dosage of isoniazid and tacrolimus, respectively. Conclusion: Our systematic review supports a promising role for the IGRA-CMVs for adjustment of the duration of anti-CMV antiviral prophylaxis in SOT recipients. There are limited data to support the use of IFAs other than IGRA-CMVs for adjustment of immunosuppressive or anti-infective agents. Further multicenter randomized clinical trials using IFAs other than IGRA-CMVs may help in personalized immunosuppressive or prophylactic anti-infective therapy in SOT recipients.
Keywords: anti-infective agent; immune functional assay; immune system; immunosuppressive agent; transplantation.
Copyright © 2020 Rezahosseini, Møller, Knudsen, Sørensen, Perch, Gustafsson, Rasmussen, Ostrowski and Nielsen.
Figures
References
-
- Drabe CH, Sorensen SS, Rasmussen A, Perch M, Gustafsson F, Rezahosseini O, et al. Immune function as predictor of infectious complications and clinical outcome in patients undergoing solid organ transplantation (the ImmuneMo:SOT study): a prospective non-interventional observational trial. BMC Infect Dis. (2019) 19:573. 10.1186/s12879-019-4207-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Enderby C, Keller CA. An overview of immunosuppression in solid organ transplantation. Am J Manag Care. (2015) 21:s12–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

