A Novel Bayesian Approach for EEG Source Localization
- PMID: 33178259
- PMCID: PMC7647781
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8837954
A Novel Bayesian Approach for EEG Source Localization
Abstract
We propose a new method for EEG source localization. An efficient solution to this problem requires choosing an appropriate regularization term in order to constraint the original problem. In our work, we adopt the Bayesian framework to place constraints; hence, the regularization term is closely connected to the prior distribution. More specifically, we propose a new sparse prior for the localization of EEG sources. The proposed prior distribution has sparse properties favoring focal EEG sources. In order to obtain an efficient algorithm, we use the variational Bayesian (VB) framework which provides us with a tractable iterative algorithm of closed-form equations. Additionally, we provide extensions of our method in cases where we observe group structures and spatially extended EEG sources. We have performed experiments using synthetic EEG data and real EEG data from three publicly available datasets. The real EEG data are produced due to the presentation of auditory and visual stimulus. We compare the proposed method with well-known approaches of EEG source localization and the results have shown that our method presents state-of-the-art performance, especially in cases where we expect few activated brain regions. The proposed method can effectively detect EEG sources in various circumstances. Overall, the proposed sparse prior for EEG source localization results in more accurate localization of EEG sources than state-of-the-art approaches.
Copyright © 2020 Vangelis P. Oikonomou and Ioannis Kompatsiaris.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
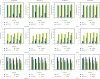
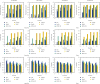

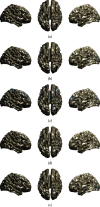


References
-
- Liu S., Cao R., Huang Y., Ouypornkochagorn T., Ji J. Time sequence learning for electrical impedance tomography using bayesian spatiotemporal priors. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. 2020;69(9):6045–6057. doi: 10.1109/tim.2020.2972172. - DOI
-
- Liu S., Huang Y., Wu H., Tan C., Jia J. Efficient multi-task structure-aware sparse bayesian learning for frequency-difference electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. 2020;20:p. 1.
-
- Sekihara K., Nagarajan S. S. Electromagnetic Brain Imaging - A Bayesian Perspective. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

