Four-dimensional impedance manometry derived from esophageal high-resolution impedance-manometry studies: a novel analysis paradigm
- PMID: 33178334
- PMCID: PMC7592175
- DOI: 10.1177/1756284820969050
Four-dimensional impedance manometry derived from esophageal high-resolution impedance-manometry studies: a novel analysis paradigm
Abstract
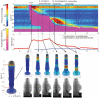
Background: This study aimed to introduce a novel analysis paradigm, referred to as 4-dimensional (4D) manometry based on biophysical analysis; 4D manometry enables the visualization of luminal geometry of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction (EGJ) using high-resolution-impedance-manometry (HRIM) data.
Methods: HRIM studies from two asymptomatic controls and one type-I achalasia patient were analyzed. Concomitant fluoroscopy images from one control subject were used to validate the calculated temporal-spatial luminal radius and time-history of intraluminal bolus volume and movement. EGJ analysis computed diameter threshold for emptying, emptying time, flow rate, and distensibility index (DI), which were compared with bolus flow time (BFT) analysis.
Results: For normal control, calculated volumes for 5 ml swallows were 4.1 ml-6.7 ml; for 30 ml swallows 21.3 ml-21.8 ml. With type-I achalasia, >4 ml of intraesophageal bolus residual was present both pre- and post-swallow. The four phases of bolus transit were clearly illustrated on the time-history of bolus movement, correlating well with the fluoroscopic images. In the control subjects, the EGJ diameter threshold for emptying was 8 mm for 5 ml swallows and 10 mm for 30 ml swallows; emptying time was 1.2-2.2 s for 5 ml swallows (BFT was 0.3-3 s) and 3.25-3.75 s for 30 ml swallows; DI was 2.4-3.4 mm2/mmHg for 5 ml swallows and 4.2-4.6 mm2/mmHg for 30 ml swallows.
Conclusions: The 4D manometry system facilitates a comprehensive characterization of dynamic esophageal bolus transit with concurrent luminal morphology and pressure from conventional HRIM measurements. Calculations of flow rate and wall distensibility provide novel measures of EGJ functionality.
Keywords: 4D manometry; esophageal manometry; esophagus; intraluminal impedance; peristalsis.
© The Author(s), 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Wenjun Kou: Crospon, Inc. (Consulting) Neelesh A. Patankar and Peter J. Kahrilas disclose no conflicts of interest Dustin A. Carlson and John E. Pandolfino hold shared intellectual property rights and ownership surrounding FLIP panometry systems, methods, and apparatus with Medtronic Inc. Dustin A. Carlson: Medtronic (speaking, consulting) John E. Pandolfino: Crospon, Inc (stock options), Given Imaging (consultant, grant, speaking), Sandhill Scientific (consulting, speaking), Takeda (speaking), Astra Zeneca (speaking), Medtronic (speaking, consulting), Torax (speaking, consulting), Ironwood (consulting), Impleo (grant).
Figures



References
-
- Ghosh SK, Janiak P, Schwizer W, et al. Physiology of the esophageal pressure transition zone: separate contraction waves above and below. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006; 290: G568–G576. - PubMed
-
- Mittal RK, Padda B, Bhalla V, et al. Synchrony between circular and longitudinal muscle contractions during peristalsis in normal subjects. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006; 290: G431–G438. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

