Influence of Optimization Design Based on Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things on the Electrocardiogram Monitoring System
- PMID: 33178407
- PMCID: PMC7609146
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8840910
Influence of Optimization Design Based on Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things on the Electrocardiogram Monitoring System
Abstract
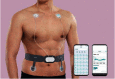
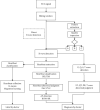
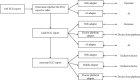
With the increasing emphasis on remote electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring, a variety of wearable remote ECG monitoring systems have been developed. However, most of these systems need improvement in terms of efficiency, stability, and accuracy. In this study, the performance of an ECG monitoring system is optimized by improving various aspects of the system. These aspects include the following: the judgment, marking, and annotation of ECG reports using artificial intelligence (AI) technology; the use of Internet of Things (IoT) to connect all the devices of the system and transmit data and information; and the use of a cloud platform for the uploading, storage, calculation, and analysis of patient data. The use of AI improves the accuracy and efficiency of ECG reports and solves the problem of the shortage and uneven distribution of high-quality medical resources. IoT technology ensures the good performance of remote ECG monitoring systems in terms of instantaneity and rapidity and, thus, guarantees the maximum utilization efficiency of high-quality medical resources. Through the optimization of remote ECG monitoring systems with AI and IoT technology, the operating efficiency, accuracy of signal detection, and system stability have been greatly improved, thereby establishing an excellent health monitoring and auxiliary diagnostic platform for medical workers and patients.
Copyright © 2020 Ming Yin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
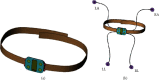

Similar articles
-
[Artificial intelligence in wearable electrocardiogram monitoring].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Dec 25;40(6):1084-1092. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202301032. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 38151930 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Design and Development of ECG Monitoring Cloud Platform Based on the Internet of Things Electrocardiograph].Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2024 Mar 30;48(2):228-231. doi: 10.12455/j.issn.1671-7104.230247. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38605627 Chinese.
-
Reliable ECG Anomaly Detection on Edge Devices for Internet of Medical Things Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;25(8):2496. doi: 10.3390/s25082496. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40285186 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Named Data Networking Mobility Methodology in a Merged Cloud Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 3;22(17):6668. doi: 10.3390/s22176668. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36081126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Survey on Artificial Intelligence Aided Internet-of-Things Technologies in Emerging Smart Libraries.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Apr 13;22(8):2991. doi: 10.3390/s22082991. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35458974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychometric assessment of the Persian translated version of the "medical artificial intlligence readiness scale for medical students".PLoS One. 2025 May 12;20(5):e0323543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323543. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40354459 Free PMC article.
-
An IoT and Fog Computing-Based Monitoring System for Cardiovascular Patients with Automatic ECG Classification Using Deep Neural Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Dec 21;20(24):7353. doi: 10.3390/s20247353. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33371514 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

