Baseline plasma levels of soluble PD-1, PD-L1, and BTN3A1 predict response to nivolumab treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a step toward a biomarker for therapeutic decisions
- PMID: 33178494
- PMCID: PMC7595592
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1832348
Baseline plasma levels of soluble PD-1, PD-L1, and BTN3A1 predict response to nivolumab treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a step toward a biomarker for therapeutic decisions
Abstract
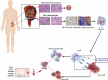
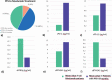
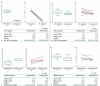
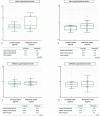
Despite a proportion of renal cancer patients can experiment marked and durable responses to immune-checkpoint inhibitors, the treatment efficacy is widely variable and identifying the patient who will benefit from immunotherapy remains an issue. We performed a prospective study to investigate if soluble forms of the immune-checkpoints PD-1 (sPD-1), PD-L1 (sPD-L1), pan-BTN3As, BTN3A1, and BTN2A1, could be candidate to predict the response to immune-checkpoint blockade therapy. We evaluated the plasma levels in a learning cohort of metastatic clear cell renal carcinoma (mccRCC) patients treated with the anti-PD-1 agent nivolumab by ad hoc developed ELISA's. Using specific cut-offs determined through ROC curves, we showed that high baseline levels of sPD-1 (>2.11 ng/ml), sPD-L1 (>0.66 ng/ml), and sBTN3A1 (>6.84 ng/ml) were associated with a longer progression-free survival (PFS) to nivolumab treatment [median PFS, levels above thresholds: sPD-1, 20.7 months (p < .0001); sPD-L1, 19 months (p < .0001); sBTN3A1, 17.5 months (p = .002)]. High sPD-1 and sBTN3A1 levels were also associated with best overall response by RECIST and objective response of >20%. The results were confirmed in a validation cohort of 20 mccRCC patients. The analysis of plasma dynamic changes after nivolumab showed a statistically significant decrease of sPD-1 after 2 cycles (Day 28) in the long-responder patients. Our study revealed that the plasma levels of sPD-1, sPD-L1, and sBTN3A1 can predict response to nivolumab, discriminating responders from non-responders already at therapy baseline, with the advantages of non-invasive sample collection and real-time monitoring that allow to evaluate the dynamic changes during cancer evolution and treatment.
Keywords: BTN2A1; BTN3A1; PD-1; PD-L1; butyrophilins; circulating immune checkpoints; immunotherapy response; predictive biomarker; renal cell carcinoma; soluble immune-checkpoints.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published with license by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Figures

References
-
- Incorvaia L, Bronte G, Bazan V, Badalamenti G, Rizzo S, Pantuso G, Natoli C, Russo A. Beyond evidence-based data: scientific rationale and tumor behavior to drive sequential and personalized therapeutic strategies for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(16):21259–21271. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7267. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
