Human microRNAs in host-parasite interaction: a review
- PMID: 33178551
- PMCID: PMC7644590
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-020-02498-6
Human microRNAs in host-parasite interaction: a review
Abstract
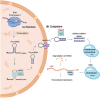
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of small noncoding RNA molecules with significant capacity to regulate the gene expression at the post-transcriptional level in a sequence-specific manner either through translation repression or mRNA degradation triggering a fine-tuning biological impact. They have been implicated in several processes, including cell growth and development, signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation, metabolism, apoptosis, inflammation, and immune response modulation. However, over the last few years, extensive studies have shown the relevance of miRNAs in human pathophysiology. Common human parasitic diseases, such as Malaria, Leishmaniasis, Amoebiasis, Chagas disease, Schistosomiasis, Toxoplasmosis, Cryptosporidiosis, Clonorchiasis, and Echinococcosis are the leading cause of death worldwide. Thus, identifying and characterizing parasite-specific miRNAs and their host targets, as well as host-related miRNAs, are important for a deeper understanding of the pathophysiology of parasite-specific diseases at the molecular level. In this review, we have demonstrated the impact of human microRNAs during host-parasite interaction as well as their potential to be used for diagnosis and prognosis purposes.
Keywords: Biomarker; Human parasitic diseases; Pathophysiology; Prognosis; microRNAs.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNAs: Critical Players during Helminth Infections.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 25;11(1):61. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010061. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: master regulators in host-parasitic protist interactions.Open Biol. 2022 Jun;12(6):210395. doi: 10.1098/rsob.210395. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Open Biol. 2022. PMID: 35702995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of hepatic microRNA expression profiles with Clonorchis sinensis infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Nov 30;16(1):724. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-2058-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27899092 Free PMC article.
-
Application of small RNA technology for improved control of parasitic helminths.Vet Parasitol. 2015 Aug 15;212(1-2):47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Vet Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26095949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of microRNAs in the Infection by T. gondii in Humans.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 May 14;11:670548. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.670548. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34055667 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
microRNAs: Critical Players during Helminth Infections.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 25;11(1):61. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010061. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative microRNA profiling of Trypanosoma cruzi infected human cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jun 21;13:1187375. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1187375. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37424776 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the role of miR-186 in SIRT1 regulation in adipocytes: implications for adipogenesis and inflammation in obesity.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 Jan 8;24(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s40200-024-01525-0. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 39801683
-
Novel miRNA biomarkers for alveolar echinococcosis: sequencing and clinical validation.Parasitology. 2024 Nov;151(13):1473-1486. doi: 10.1017/S0031182024001367. Parasitology. 2024. PMID: 39420785 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of nanotechnologies for miRNA-based cancer therapeutics: current advances and future perspectives.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 27;11:1208547. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1208547. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37576994 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

