A Pilot Study of Cardiac MRI in Breast Cancer Survivors After Cardiotoxic Chemotherapy and Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy
- PMID: 33178571
- PMCID: PMC7596658
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.506739
A Pilot Study of Cardiac MRI in Breast Cancer Survivors After Cardiotoxic Chemotherapy and Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy
Abstract
Purpose/objectives: Node-positive breast cancer patients often receive chemotherapy and regional nodal irradiation. The cardiotoxic effects of these treatments, however, may offset some of the survival benefit. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) is an emerging modality to assess cardiac injury. This is a pilot trial assessing cardiac damage using CMR in patients who received anthracycline-based chemotherapy and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT) regional nodal irradiation using heart constraints.
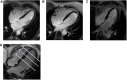
Materials and methods: Node-positive breast cancer patients (2000-2008) treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy and 3DCRT regional nodal irradiation (including the internal mammary chain nodes) with heart ventricular constraints (V25 < 10%) were invited to participate. Cardiac tissues were contoured and analyzed separately for whole heart (pericardium) and for combined ventricles and left atrium (myocardium). CMR obtained ventricular function/dimensions, late gadolinium enhancement (LGE), global longitudinal strain (GLS), and extracellular volume fraction (ECV) as measures of cardiac injury and/or early fibrosis. CMR parameters were correlated with dose-volume constraints using Spearman correlations.
Results: Fifteen left-sided and five right-sided patients underwent CMR. Median diagnosis age was 50 (32-77). No patients had baseline cardiac disease before regional nodal irradiation. Median time after 3DCRT was 8.3 years (5.2-14.4). Median left-sided mean heart dose (MHD) was 4.8 Gy (1.1-11.2) and V25 was 5.7% (0-12%). Median left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 63%. No abnormal LGE was observed. No correlations were seen between whole heart doses and LVEF, LV mass, GLS, or LV dimensions. Increasing ECV did not correlate with increased heart or ventricular doses. However, correlations between higher LV mass and ventricular mean dose, V10, and V25 were seen.
Conclusion: At a median follow-up of 8.3 years, this cohort of node-positive breast cancer patients who received anthracycline-based chemotherapy and regional nodal irradiation had no clinically abnormal CMR findings. However, correlations between ventricular mean dose, V10, and V25 and LV mass were seen. Larger corroborating studies that include advanced techniques for measuring regional heart mechanics are warranted.
Keywords: 3D conformal radiation therapy; breast cancer; cardiac MRI; cardiotoxicity; radiation therapy.
Copyright © 2020 Bergom, Rubenstein, Wilson, Welsh, Ibrahim, Prior, Schottstaedt, Eastwood, Zhang, Currey, Puckett, Strande, Bradley and White.
Figures
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG), Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, Arriagada R, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. (2011) 378:1707–16. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61629-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EBCTCG (Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group), McGale P, Taylor C, Correa C, Cutter D, Duane F, et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet. (2014) 383:2127–35. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60488-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

