Case Report: Late Onset of Myelodysplastic Syndrome From Donor Progenitor Cells After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Which Lessons Can We Draw From the Reported Case?
- PMID: 33178592
- PMCID: PMC7591784
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.564521
Case Report: Late Onset of Myelodysplastic Syndrome From Donor Progenitor Cells After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Which Lessons Can We Draw From the Reported Case?
Abstract
Background: Myelodysplastic syndromes and acute leukemias after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) are mainly caused by recurrence of the primitive leukemic clones. More rarely, they originate from donor hematopoietic stem cells, developing the so-called donor cell leukemia (DCL) or myelodysplastic syndromes (DC-MDSs). DCL and DC-MDS can be considered as an in vivo model of leukemogenesis, and even if the pathogenetic mechanisms remain speculative, a genetic predisposition of donor progenitor cells, an altered host microenvironment, and the impairment of immune surveillance are considered the main causes.
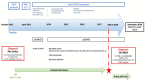
Case presentation: We report a case of DC-MDS diagnosed 5 years after an allo-SCT from a matched related donor (patient's sister) in a patient with Philadelphia chromosome-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ B-ALL). The sex-mismatch allowed us to identify the donor cell origin. At the onset, the DC-MDS was characterized by chromosome seven monosomy and NRAS, RUNX1, and BCOR mutations. Because of a familiar history of colorectal neoplasia and the variant allele frequency (VAF) of NRAS mutation at the onset, this mutation was searched on germline DNA in both the donor and the recipient, but the result was negative. Moreover, after transplant (+4 months), the patient developed severe and long-lasting chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), requiring multiple lines of treatments. Because of the severe immunosuppression, recurrent infections occurred and, lately, the patient died due to septic shock.
Conclusion: This case report highlights the need, whenever possible, to evaluate the donor origin of the posttransplant myelodysplasia and acute leukemias. The potential key role of the impaired immune surveillance and of long-lasting immunosuppression appears to be emerging in the development of this case of DC-MDS. Finally, this case reminds the importance to investigate the familiar genetic predisposition in donors with a familiar history of neoplasia.
Keywords: donor cell myelodysplasia; immunosuppression; immunosurveillance; leukemogenesis; stem cells; transplant.
Copyright © 2020 Farina, Bernardi, Gandolfi, Zanaglio, Morello, Turra, Zollner, Gramegna, Rambaldi, Cattina, Polverelli, Malagola and Russo.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

