Acute Cervical Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis in a Child With Lipopolysaccharide-Responsive-Beige-Like-Anchor-Protein (LRBA) Deficiency: A New Complication of a Rare Disease
- PMID: 33178652
- PMCID: PMC7596261
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.580963
Acute Cervical Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis in a Child With Lipopolysaccharide-Responsive-Beige-Like-Anchor-Protein (LRBA) Deficiency: A New Complication of a Rare Disease
Abstract
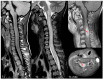
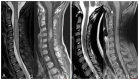
Lipopolysaccharide responsive beige-like anchor protein (LRBA) deficiency is a primary immunodeficiency disorder (PID) that can cause a common variable immunodeficiency (CVID)-like disease. The typical features of the disease are autoimmunity, chronic diarrhea, and hypogammaglobulinemia. Neurological complications are also reported in patients affected by LRBA deficiency. We describe a 7-year old female with an acute cervical longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) as a feature of LRBA deficiency. This is the first case of LETM associated with LRBA deficiency described in literature.
Keywords: acute cervical longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis; autommunity; common variable immune deficiency (CVID); lipopolysaccharide responsive beige-like anchor protein (LRBA); myelitis.
Copyright © 2020 Chinello, Mauro, Cantalupo, Talenti, Mariotto, Balter, De Bortoli, Vitale, Zaccaron, Bonetti, Di Carlo, Barzaghi and Cesaro.
Figures
References
-
- EnsemblGenomeBrowser (2015). Available online at: http://www.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Transcript/Sequence_Protein?db=core;... (accessed June 30, 2020).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

