Process Characterization by Definitive Screening Design Approach on DNA Vaccine Production
- PMID: 33178673
- PMCID: PMC7593689
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.574809
Process Characterization by Definitive Screening Design Approach on DNA Vaccine Production
Abstract
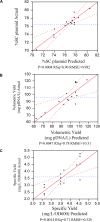
Plasmid DNA is a vital biological tool for molecular cloning and transgene expression of recombinant proteins; however, decades ago, it has become an exceptionally appealing as a potential biopharmaceutical product as genetic immunization for animal and human use. The demand for large-quantity production of DNA vaccines also increases. Thus, we, herein, presented a systematic approach for process characterization of fed-batch Escherichia coli DH5α fermentation producing a porcine DNA vaccine. Design of Experiments (DoE) was employed to determine process parameters that have impacts on a critical quality attribute of the product, which is the active form of plasmid DNA referred as supercoiled plasmid DNA content, as well as the performance attributes, which are volumetric yield and specific yield from fermentation. The parameters of interest were temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, cultivation time, and feed rate. Using the definitive-screening design, there were 16 runs, including 3 additional center points to create the predictive model, which then was used to simulate the operational ranges for capability analysis.
Keywords: DNA vaccine; critical process parameter; critical quality attributes; definitive screening design; process characterization.
Copyright © 2020 Hocharoen, Noppiboon and Kitsubun.
Figures



References
-
- Agrilabs (2017). First DNA Vaccine Licensed for Chickens. New York, NY: Cision PR newswire.
-
- Burnham K. P., Anderson D. R. (2004). Multimodel inference: understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociol. Methods Res. 33 261–304. 10.1177/0049124104268644 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

