Syndecan-4 Modulates Cell Polarity and Migration by Influencing Centrosome Positioning and Intracellular Calcium Distribution
- PMID: 33178691
- PMCID: PMC7593626
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.575227
Syndecan-4 Modulates Cell Polarity and Migration by Influencing Centrosome Positioning and Intracellular Calcium Distribution
Abstract
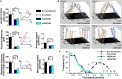
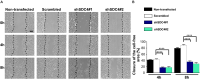
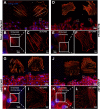
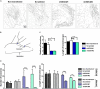
Efficient cell migration requires cellular polarization, which is characterized by the formation of leading and trailing edges, appropriate positioning of the nucleus and reorientation of the Golgi apparatus and centrosomes toward the leading edge. Migration also requires the development of an asymmetrical front-to-rear calcium (Ca2+) gradient to regulate focal adhesion assembly and actomyosin contractility. Here we demonstrate that silencing of syndecan-4, a transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan, interferes with the correct polarization of migrating mammalian myoblasts (i.e., activated satellite stem cells). In particular, syndecan-4 knockdown completely abolished the intracellular Ca2+ gradient, abrogated centrosome reorientation and thus decreased cell motility, demonstrating the role of syndecan-4 in cell polarity. Additionally, syndecan-4 exhibited a polarized distribution during migration. Syndecan-4 knockdown cells exhibited decreases in the total movement distance during directional migration, maximum and vectorial distances from the starting point, as well as average and maximum cell speeds. Super-resolution direct stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy images of syndecan-4 knockdown cells revealed nanoscale changes in the actin cytoskeletal architecture, such as decreases in the numbers of branches and individual branch lengths in the lamellipodia of the migrating cells. Given the crucial importance of myoblast migration during embryonic development and postnatal muscle regeneration, we conclude that our results could facilitate an understanding of these processes and the general role of syndecan-4 during cell migration.
Keywords: actin; calcium; cell migration; cell polarity; centrosome; proteoglycan; super-resolution microscopy; syndecan-4.
Copyright © 2020 Becsky, Szabo, Gyulai-Nagy, Gajdos, Bartos, Balind, Dux, Horvath, Erdelyi, Homolya and Keller-Pinter.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Myoblast Migration and Directional Persistence Affected by Syndecan-4-Mediated Tiam-1 Expression and Distribution.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 27;21(3):823. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030823. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32012800 Free PMC article.
-
The reorientation of cell nucleus promotes the establishment of front-rear polarity in migrating fibroblasts.J Mol Biol. 2013 Jun 12;425(11):2039-2055. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.02.034. Epub 2013 Mar 21. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23524135
-
Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex-mediated actin-dependent nuclear positioning orients centrosomes in migrating myoblasts.Nucleus. 2015;6(1):77-88. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2015.1004947. Nucleus. 2015. PMID: 25587885 Free PMC article.
-
Syndecan-4 in Tumor Cell Motility.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 1;13(13):3322. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133322. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34282767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syndecan proteoglycan contributions to cytoskeletal organization and contractility.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009 Aug;19(4):479-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.00941.x. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2009. PMID: 19538537 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix: Brick and mortar in the skeletal muscle stem cell niche.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 29;10:1056523. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1056523. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36523505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial and single-cell colocalisation analysis reveals MDK-mediated immunosuppressive environment with regulatory T cells in colorectal carcinogenesis.EBioMedicine. 2024 May;103:105102. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105102. Epub 2024 Apr 12. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 38614865 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial multiomic landscape of the human placenta at molecular resolution.Nat Med. 2024 Dec;30(12):3495-3508. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03073-9. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 39567716
-
Unravelling the Effects of Syndecan-4 Knockdown on Skeletal Muscle Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 8;24(8):6933. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086933. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108098 Free PMC article.
-
RhoA Is a Crucial Regulator of Myoblast Fusion.Cells. 2023 Nov 21;12(23):2673. doi: 10.3390/cells12232673. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baciu P. C., Saoncella S., Lee S. H., Denhez F., Leuthardt D., Goetinck P. F. (2000). Syndesmos, a protein that interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of syndecan-4, mediates cell spreading and actin cytoskeletal organization. J. Cell Sci. 113(Pt 2) 315–324. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

