Brain imaging biomarkers of carotid artery disease
- PMID: 33178809
- PMCID: PMC7607077
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-1939
Brain imaging biomarkers of carotid artery disease
Abstract
Extracranial carotid artery atherosclerotic disease is a major contributor to ischemic stroke. Carotid atherosclerotic disease can present with a spectrum of findings ranging from mild carotid intima-media thickness to high-risk vulnerable carotid plaque features and carotid stenosis. Before leading to clinically overt stroke or transient ischemic attack, there may be other markers of downstream ischemia secondary to carotid atherosclerotic disease. In this review article, we will review some of the imaging findings that may be seen downstream to carotid artery disease on various imaging modalities, including hemodynamic and perfusional abnormalities which may be seen on CT, MR, or using other advanced imaging techniques, white matter hyperintensities on brain imaging, silent or covert brain infarctions, cerebral microbleeds, and regional and generalized cerebral volume loss. Many of these imaging findings are seen routinely on brain magnetic resonance imaging in patients without overt clinical symptoms. Despite frequently being asymptomatic, many of these imaging findings are also strongly associated with increased risk of future stroke, cognitive impairment, and even mortality. We will review the existing evidence underpinning the associations between these frequently encountered imaging findings and carotid artery atherosclerotic disease. Future validation of these imaging findings could lead to them being powerful biomarkers of cerebrovascular health.
Keywords: Carotid artery diseases; cerebrovascular disorders; cognitive dysfunction; magnetic resonance imaging; stroke.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-1939). The series “Carotid Artery Stenosis and Stroke: Prevention and Treatment Part I” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. HB reports grants from Association of University Radiologists-General Electric Radiology Research Fellowship, during the conduct of the study. AG reports non-financial support from GE Healthcare and non-financial support from Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc., outside the submitted work. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



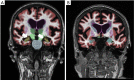
References
-
- Brott TG, Halperin JL, Abbara S, et al. 2011 ASA/ACCF/AHA/AANN/AANS/ACR/ASNR/CNS/SAIP/SCAI/SIR/SNIS/SVM/SVS guideline on the management of patients with extracranial carotid and vertebral artery disease: A report of the American college of cardiology foundation/American heart association task force on practice guidelines, and the American stroke association, American association of neuroscience nurses, American association of neurological surgeons, American college of radiology, American society of neuroradiology, congress of neurological surgeons, society of atherosclerosis imaging and prevention, society for cardiovascular angiography and interventions, society of interventional radiology, society of neurointerventional surgery, society for vascular medicine, and society for vascular surgery developed in collaboration with the American academy of neurology and society of cardiovascular computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;57:e16-e94. 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.11.006 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
