Registration accuracy with the low dose kilovoltage cone-beam CT: A phantom study
- PMID: 33178952
- PMCID: PMC7592495
- DOI: 10.1259/bjro.20190028
Registration accuracy with the low dose kilovoltage cone-beam CT: A phantom study
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate low-dose kilovoltage cone-beam CT (kV-CBCT) for image-guided radiotherapy, with a particular focus on the accuracy of image registration with low-dose protocols.
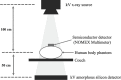
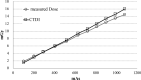
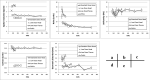
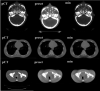
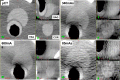
Methods: Imaging doses were measured with a NOMEX semiconductor detector positioned at the front of head, thorax, and pelvis human body phantoms while kV-CBCT scans were acquired at different tube currents. Aspects of image quality (spatial resolution, noise, uniformity, contrast, geometric distortion, and Hounsfield unit sensitivity) and image registration accuracy using bone and soft tissue were evaluated.
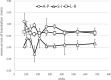
Results: With preset and the lowest tube currents, the imaging doses were 0.16 and 0.08 mGy, 5.29 and 2.80 mGy, and 18.23 and 2.69 mGy for head, thorax, and pelvis, respectively. Noise was the only quality aspect directly dependent on tube current, being increased by 1.5 times with a tube current half that of the preset in head and thorax, and by 2.2 times with a tube current 1/8 of the preset in the pelvis. Accurate auto-bone matching was performed within 1 mm at the lowest tube current. The auto-soft tissue matching could not be performed with the lowest tube current; however, manual-soft tissue matching could still be performed within 2 mm or less.
Conclusion: Noise was the only image quality aspect dependent on the imaging dose. Auto-bone and manual-soft tissue matching could still be performed at the lowest imaging dose.
Advances in knowledge: When optimizing kV-CBCT imaging dose, the impact on bone and soft tissue image registration accuracy should be evaluated.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology.
Figures
References
-
- MR Ay, Shahriari M, Sarkar S, Ghafarian P. Measurement of organ dose in abdomen-pelvis CT exam as a function of mA, KV and scanner type by Monte Carlo method. Iran. J. Radiat. Res 2004; 1: 187–94.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

