IgG4-related disease with multiple organs involvement was effectively controlled by glucocorticoids: a case report
- PMID: 33178994
- PMCID: PMC7608720
- DOI: 10.21037/acr-20-43
IgG4-related disease with multiple organs involvement was effectively controlled by glucocorticoids: a case report
Abstract
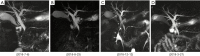
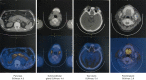
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related disease is a rare autoimmune disease involving multiple organs and tissues. A diagnosis of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is mainly based on serum IgG4 concentration, imaging, pathology, and effective glucocorticoids therapy. In this paper, we report a 53-year-old male with typical signs and symptoms of IgG4-RD successfully treated with glucocorticoids. This patient had experienced bilateral mumps for more than 8 months and intermittent abdominal pain spreading to his lower back for 2 months before his admission. During his hospitalization, based on the characteristic appearance of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), and computed tomography with positron emission tomography, a diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP), cholangitis with biliary obstruction, lachrymal adenitis, and submandibular adenitis was made. A high serum IgG4 concentration further supported a diagnosis of IgG4-RD. Then, the treatment was promptly initiated with corticosteroids. MRI, MRCP, and IgG4 concentration were re-examined during his follow up, suggesting that glucocorticoid treatment resulted in a resolution of his disease. The dosage of glucocorticoid had been gradually decreased. Now, he is stable with oral low-dose glucocorticoids. Certainly, long-term follow up of this patient with such a rare disease is very essential to observe the possibility of disease recurrence and glucocorticoids related complications.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD); Mikulicz’s disease (MD); autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP); biliary cholangitis; glucocorticoids.
2020 AME Case Reports. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/acr-20-43). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
