Gastro-esophageal reflux disease and Barrett's esophagus: an overview with an histologic diagnostic approach
- PMID: 33179616
- PMCID: PMC7931578
- DOI: 10.32074/1591-951X-162
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease and Barrett's esophagus: an overview with an histologic diagnostic approach
Abstract
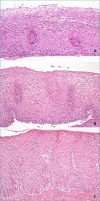
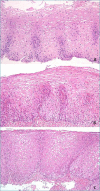
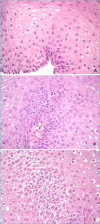
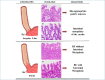
The first part of this overview on non-neoplastic esophagus is focused on gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD) and Barrett's esophagus. In the last 20 years much has changed in histological approach to biopsies of patients with gastro-esophageal reflux disease. In particular, elementary histologic lesions have been well defined and modality of evaluation and grade are detailed, their sensitivity and specificity has been evaluated and their use has been validated by several authors. Also if there is not a clinical indication to perform biopsies in patient with GERD, the diagnosis of microscopic esophagitis, when biopsies are provided, can be performed by following simple rules for evaluation which allow pathologists to make the diagnosis with confidence. On the other hand, biopsies are required for the diagnosis of Barrett's esophagus. This diagnosis is the synthesis of endoscopic picture (which has to be provided with the proper description on extent and with adequate biopsies number) and histologic pattern. The current guidelines and expert opinions for the correct management of these diagnosis are detailed.
Keywords: Barrett’s esophagus; gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD); histology; intestinal metaplasia of the cardia; microscopic esophagitis.
Copyright © 2020 Società Italiana di Anatomia Patologica e Citopatologia Diagnostica, Divisione Italiana della International Academy of Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mastracci L, Bruzzone M, Pacella E, et al. The contribution of intraepithelial inflammatory cells to the histological diagnosis of microscopic esophagitis. Esophagus 2016;13:80-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-015-0501-9 10.1007/s10388-015-0501-9 - DOI
-
- Lucendo AJ, Navarro M, Comas C, et al. Immunophenotypic characterization and quantification of the epithelial inflammatory infiltrate in eosinophilic esophagitis through stereology: an analysis of the cellular mechanisms of the disease and the immunologic capacity of the esophagus. Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:598-606. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.pas.0000213392.49698.8c 10.1097/01.pas.0000213392.49698.8c - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eusebi LH, Ratnakumaran R, Yuan Y, et al. Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms: a meta-analysis. Gut. 2018;67:430-40. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313589 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313589 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, et al. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900-20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00630.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pace F, Bazzoli F, Fiocca R, et al. The Italian validation of the Montreal Global definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009;21:394-408. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0b013e32830a70e2 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32830a70e2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

