Using Wearable Devices to Monitor Physical Activity in Patients Undergoing Aortic Valve Replacement: Protocol for a Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 33180023
- PMCID: PMC7691084
- DOI: 10.2196/20072
Using Wearable Devices to Monitor Physical Activity in Patients Undergoing Aortic Valve Replacement: Protocol for a Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background: In last few decades, several tools have been developed to measure physical function objectively; however, their use has not been well established in clinical practice.
Objective: This study aims to describe the preoperative physical function and to assess and compare 6-month postoperative changes in the physical function of patients undergoing treatment for aortic stenosis with either surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) or transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). The study also aims to evaluate the feasibility of wearable devices in assessing physical function in such patients.
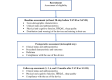
Methods: This is a prospective observational study. The enrollment will be conducted 1 month before patients' SAVR/TAVR. Patients will be provided with the wearable device at baseline (activity tracker device, Garmin vívoactive 3). They will be trained in the use of the device, and they will be requested to wear it on the wrist of their preferred hand until 12 months after SAVR/TAVR. After baseline assessment, they will undergo 4 follow-up assessments at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after SAVR/TAVR. At baseline and each follow-up, they will undergo a set of standard and validated tests to assess physical function, health-related quality of life, and sleep quality.
Results: The ethics committee of Vicenza in Veneto Region in Italy approved the study (Protocol No. 943; January 4, 2019). As of October 2020, the enrollment of participants is ongoing.
Conclusions: The use of the wearable devices for real-time monitoring of physical activity of patients undergoing aortic valve replacement is a promising opportunity for improving the clinical management and consequently, the health outcomes of such patients.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov NCT03843320; https://tinyurl.com/yyareu5y.
International registered report identifier (irrid): DERR1-10.2196/20072.
Keywords: physical function; surgical aortic valve replacement; transcatheter aortic valve replacement; wearable devices.
©Giulia Lorenzoni, Danila Azzolina, Chiara Fraccaro, Alessandro Di Liberti, Augusto D'Onofrio, Chiara Cavalli, Tommaso Fabris, Gianpiero D'Amico, Giorgia Cibin, Luca Nai Fovino, Honoria Ocagli, Gino Gerosa, Giuseppe Tarantini, Dario Gregori. Originally published in JMIR Research Protocols (http://www.researchprotocols.org), 12.11.2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Ueshima D, Fovino Luca Nai, D'Amico Gianpiero, Brener SJ, Esposito G, Tarantini G. Transcatheter versus surgical aortic valve replacement in low- and intermediate-risk patients: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2019 Jul;34(3):216–225. doi: 10.1007/s12928-018-0546-5. - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

