Predictive factors of early progression after CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 33180899
- PMCID: PMC7686887
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003001
Predictive factors of early progression after CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
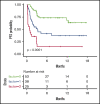
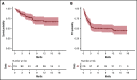
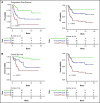
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as an option for relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas that have failed 2 lines of therapy. Failures usually occur early after infusion. The purpose of our study was to identify factors that may predict failure, particularly early progression (EP), within the first month after infusion. Characteristics of 116 patients were analyzed at the time of decision (TD) to use commercial CAR (axicabtagene ciloleucel, n = 49; tisagenlecleucel n = 67) and at the time of treatment (TT), together with total metabolic tumor volume (TMTV) at TT. With a median follow-up of 8.2 months, 55 patients failed treatment; 27 (49%) were early progressors. The estimated 12-month progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 47.2% (95% confidence interval [CI], 38.0-58.6) and 67.0% (95% CI, 57-79), respectively. Univariate analyses for PFS and OS identified Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) ≥2, stage III/IV disease, extranodal (EN) sites ≥2, elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), increased C-reactive protein (CRP), high International Prognostic Index at TD and at TT, as well as increased CRP, bulky mass, and high TMTV at TT, as risk factors. Multivariate analyses for PFS, EP, and OS identified elevated LDH and EN sites ≥2 at TD and the same predictors at TT (ie, increased CRP, EN sites ≥2, and TMTV >80 mL). In summary, risk factors identified for early progression at TD and at TT were EN involvement (≥2 sites) and lymphoma burden (LDH, TMTV).
© 2020 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: R.D.B. has served on advisory boards for and received honoraria from Gilead Sciences and Novartis. L.O. has served on an advisory board for and received honoraria from Janssen Pharmaceuticals outside of the submitted work. P.F. has received honoraria from, had travel accommodations paid by, and has acted in a consulting/advisory role for Roche/Genentech, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Gilead Sciences, and AbbVie. S.L.G. has acted in an advisory role for and received honoraria from Celgene, Roche, Gilead Sciences, Epizyme, Bristol Myers Squibb, Bayer, and Novartis and has received honoraria from Janssen Pharmaceuticals. L.Y. has received honoraria from, had travel accommodations paid by, and has acted in a consulting/advisory role for Roche/Genentech, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Gilead Sciences, and AbbVie. O.C. has received research funding from Roche, Takeda, and Gilead Sciences and has served on advisory boards for and received honoraria from Celgene, Roche, Takeda, Gilead Sciences, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, AbbVie, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals outside of the submitted work. C.T. has received honoraria from Roche, Amgen, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Celgene, and Gilead Sciences/Kyte; has acted in a consulting/advisory role from Roche, Gilead Sciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Celgene, and Novartis; and has received research funding from and had travel, accommodation, and expenses paid by Roche and Novartis. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Prognostic value of FDG-PET/CT response for patient selection before chimeric antigen receptor-T-cells therapy in non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Hematol Oncol. 2022 Oct;40(4):796-800. doi: 10.1002/hon.2965. Epub 2022 Jan 23. Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35044695 No abstract available.
References
-
- Van Den Neste E, Schmitz N, Mounier N, et al. Outcomes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients relapsing after autologous stem cell transplantation: an analysis of patients included in the CORAL study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(2):216-221. - PubMed
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45-56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

