COVID-19, plasma, and hypogammaglobulinemia
- PMID: 33180920
- PMCID: PMC7702476
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020008963
COVID-19, plasma, and hypogammaglobulinemia
Abstract
In this issue of Blood,
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
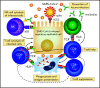
Comment on
-
Convalescent plasma therapy for B-cell-depleted patients with protracted COVID-19.Blood. 2020 Nov 12;136(20):2290-2295. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020008423. Blood. 2020. PMID: 32959052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gharbharan A, Jordans CCE, Geurtsvankessel C, et al. Convalescent plasma for COVID-19. A randomized clinical trial [published online ahead of print 3 July 2020]. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.07.01.20139857.
-
- Avendano-Sola C, Ramos-Martinez A, Munez-Rubio E, et al. Convalescent plasma for COVID-19: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial [published online ahead of print 1 September 2020]. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.08.26.20182444.
-
- Joyner MJ, Senefeld JW, Klassen SA, et al. Effect of convalescent plasma on mortality among hospitalized patients with COVID-19: initial three-month experience [published online ahead of print 12 August 2020]. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2020.08.12.20169359.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

