Mechanical Allodynia Circuitry in the Dorsal Horn Is Defined by the Nature of the Injury
- PMID: 33181066
- PMCID: PMC7806207
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.10.027
Mechanical Allodynia Circuitry in the Dorsal Horn Is Defined by the Nature of the Injury
Abstract
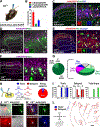
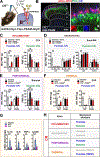
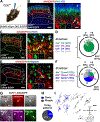
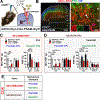
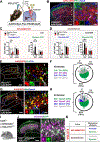
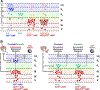
The spinal dorsal horn is a major site for the induction and maintenance of mechanical allodynia, but the circuitry that underlies this clinically important form of pain remains unclear. The studies presented here provide strong evidence that the neural circuits conveying mechanical allodynia in the dorsal horn differ by the nature of the injury. Calretinin (CR) neurons in lamina II inner convey mechanical allodynia induced by inflammatory injuries, while protein kinase C gamma (PKCγ) neurons at the lamina II/III border convey mechanical allodynia induced by neuropathic injuries. Cholecystokinin (CCK) neurons located deeper within the dorsal horn (laminae III-IV) are important for both types of injuries. Interestingly, the Maf+ subset of CCK neurons is composed of transient vesicular glutamate transporter 3 (tVGLUT3) neurons, which convey primarily dynamic allodynia. Identification of an etiology-based circuitry for mechanical allodynia in the dorsal horn has important implications for the mechanistic and clinical understanding of this condition.
Keywords: calretinin; cholecystokinin; dorsal horn; inflammatory pain; mechanical allodynia; neural circuitry; neuropathic pain; pain; protein kinase C gamma; vesicular glutamate transporter 3.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Sensory Symphonies: How Excitatory Spinal Cord Modules Orchestrate Behavior.Neuron. 2021 Jan 6;109(1):3-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.12.012. Neuron. 2021. PMID: 33412095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alba-Delgado C, El Khoueiry C, Peirs C, Dallel R, Artola A, and Antri M (2015). Subpopulations of PKCgamma interneurons within the medullary dorsal horn revealed by electrophysiologic and morphologic approach. Pain 156, 1714–1728. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, Voisin D, and Dallel R (2020). PKCgamma interneurons, a gateway to pathological pain in the dorsal horn. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 127, 527–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

