The role of amplified in breast cancer 1 in breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 33181714
- PMCID: PMC7668486
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023248
The role of amplified in breast cancer 1 in breast cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Amplified in breast cancer 1 (AIB1) expression is known to be involved in the initiation and progression of malignant breast cancer (BC), but its prognostic role remains uncertain. This meta-analysis assessed reported studies to evaluate this relationship.
Methods: Electronic databases were systematically reviewed to collect eligible studies using pre-established criteria. Hazard ratios (HRs) or odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were pooled to estimate the impact of AIB1 protein expression on overall survival (OS) and clinicopathologic properties of BC cases.
Results: Nine eligible studies, including 6774 patients, were finally assessed by the current clinical meta-analysis. AIB1 positivity correlated with reduced OS (pooled HR = 1.409, 95% CI 1.159-1.714, P = .001). AIB1 overexpression also impacted prognosis as shown by univariate (pooled HR = 1.420, 95% CI 1.154-1.747, P = .001) and multivariate (pooled HR = 1.446, 95% CI 1.099-1.956; P = .009) analyses. Notably, subgroup analyses also revealed that AIB1 overexpression was associated with poor OS in some subgroups, such as ER-positive group (pooled HR = 1.511, 95% CI 1.138-2.006, P = .004), ER-positive without tamoxifen administration group (pooled HR = 2.338, 95% CI 1.489-3.627, P < .001), and premenopausal women group (pooled HR = 1.715, 95% CI 1.231-2.390, P = .001). Additionally, high AIB1 protein levels were associated with HER2 positivity (pooled OR = 0.331, 95% CI 0.245-0.448; P < .001), poorly differentiated histological grade (pooled OR = 0.377, 95% CI 0.317-0.448; P < .001), high Ki67 (pooled OR = 0.501, 95% CI 0.410-0.612; P < .001), presence of lymph node metastases (pooled OR = 0.866, 95% CI 0.752-0.997; P = .045), and absence of progesterone receptor (pooled OR = 1.447, 95% CI 1.190-1.759; P < .001).
Conclusions: This analysis demonstrated that AIB1 overexpression is related to aggressive phenotypes and unfavorable clinical outcomes in BC, and might involve in tamoxifen resistance. AIB1 may be a new prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in BC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
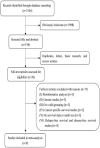
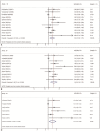

Similar articles
-
The estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 is a new putative prognostic biomarker in ER-positive/HER2-negative invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jun;175(2):305-316. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05138-7. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30796653 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and predictive importance of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 in a randomized trial comparing adjuvant letrozole and tamoxifen therapy in postmenopausal breast cancer: the Danish cohort of BIG 1-98.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Nov;166(2):481-490. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4416-0. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28766132 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic relevance of AIB1 (NCoA3) amplification and overexpression in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Feb;137(3):745-53. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2406-4. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23322234
-
The role and regulation of the nuclear receptor co-activator AIB1 in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009 Jul;116(2):225-37. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0405-2. Epub 2009 May 6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009. PMID: 19418218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of microRNA-21 overexpression in breast cancer: a meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):5622-33. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Endocrine Resistance in Estrogen-Positive Breast Cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 25;12:599586. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.599586. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33841325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Dihge L, Bendahl PO, Grabau D, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the estrogen receptor modulator amplified in breast cancer (AIB1) for predicting clinical outcome after adjuvant tamoxifen in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2008;109:255–62. - PubMed
-
- Guan XY, Xu J, Anzick SL, et al. Hybrid selection of transcribed sequences from microdissected DNA: isolation of genes within amplified region at 20q11-q13.2 in breast cancer. Can Res 1996;56:3446–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

