Induction of Durable Antitumor Response by a Novel Oncolytic Herpesvirus Expressing Multiple Immunomodulatory Transgenes
- PMID: 33182232
- PMCID: PMC7695276
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8110484
Induction of Durable Antitumor Response by a Novel Oncolytic Herpesvirus Expressing Multiple Immunomodulatory Transgenes
Abstract
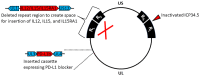
Oncolytic virotherapy is a promising new tool for cancer treatment, but direct lytic destruction of tumor cells is not sufficient and must be accompanied by strong immune activation to elicit anti-tumor immunity. We report here the creation of a novel replication-competent recombinant oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 (VG161) that carries genes coding for IL-12, IL-15, and IL-15 receptor alpha subunit, along with a peptide fusion protein capable of disrupting PD-1/PD-L1 interactions. The VG161 virus replicates efficiently and exhibits robust cytotoxicity in multiple tumor cell lines. Moreover, the encoded cytokines and the PD-L1 blocking peptide work cooperatively to boost immune cell function. In vivo testing in syngeneic CT26 and A20 tumor models reveals superior efficacy when compared to a backbone virus that does not express exogenous genes. Intratumoral injection of VG161 induces abscopal responses in non-injected distal tumors and grants resistance to tumor re-challenge. The robust anti-tumor effect of VG161 is associated with T cell and NK cell tumor infiltration, expression of Th1 associated genes in the injection site, and increased frequency of splenic tumor-specific T cells. VG161 also displayed a superb safety profile in GLP acute and repeated injection toxicity studies performed using cynomolgus monkeys. Overall, we demonstrate that VG161 can induce robust oncolysis and stimulate a robust anti-tumor immune response without sacrificing safety.
Keywords: VG161; antitumor immunity; cancer vaccine; combinatorial therapy; herpes simplex virus; immune checkpoint blockade; immunotherapy; interleukin-12; interleukin-15; oncolytic virus.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employed by, and have ownership interest (including stock, patents, etc.) in Virogin Biotech Canada Ltd. Patent applications have been filed to cover VG161 and related technologies. This study was wholly funded by Virogin Biotech Canada Ltd., but the study authors retained absolute discretion over the design and execution of the study, the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data, and the writing of the manuscript. Study funding was not conditioned on the outcome of the research.
Figures









References
-
- Liu B.L., Robinson M., Han Z.-Q., Branston R.H., English C., Reay P., McGrath Y., Thomas S.K., Thornton M., Bullock P., et al. ICP34.5 deleted herpes simplex virus with enhanced oncolytic, immune stimulating, and anti-tumour properties. Gene Ther. 2003;10:292–303. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301885. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hu J.C.C., Coffin R.S., Davis C.J., Graham N.J., Groves N., Guest P.J., Harrington K.J., James N.D., Love C.A., McNeish I., et al. A phase I study of OncoVEXGM-CSF, a second-generation oncolytic herpes simplex virus expressing granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006;12:6737–6747. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0759. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andtbacka R.H.I., Kaufman H.L., Collichio F., Amatruda T., Senzer N., Chesney J., Delman K.A., Spitler L.E., Puzanov I., Agarwala S.S., et al. Talimogene Laherparepvec Improves Durable Response Rate in Patients With Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:2780–2788. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.3377. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

