Epidemiological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: Mathematical Modeling Analyses
- PMID: 33182403
- PMCID: PMC7712303
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines8040668
Epidemiological Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination: Mathematical Modeling Analyses
Abstract
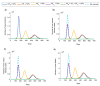
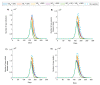
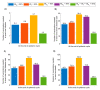
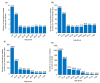
This study aims to inform SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development/licensure/decision-making/implementation, using mathematical modeling, by determining key preferred vaccine product characteristics and associated population-level impacts of a vaccine eliciting long-term protection. A prophylactic vaccine with efficacy against acquisition (VES) ≥70% can eliminate the infection. A vaccine with VES <70% may still control the infection if it reduces infectiousness or infection duration among those vaccinated who acquire the infection, if it is supplemented with <20% reduction in contact rate, or if it is complemented with herd-immunity. At VES of 50%, the number of vaccinated persons needed to avert one infection is 2.4, and the number is 25.5 to avert one severe disease case, 33.2 to avert one critical disease case, and 65.1 to avert one death. The probability of a major outbreak is zero at VES ≥70% regardless of the number of virus introductions. However, an increase in social contact rate among those vaccinated (behavior compensation) can undermine vaccine impact. In addition to the reduction in infection acquisition, developers should assess the natural history and disease progression outcomes when evaluating vaccine impact.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; epidemiology; mathematical model; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lauer S.A., Grantz K.H., Bi Q., Jones F.K., Zheng Q., Meredith H.R., Azman A.S., Reich N.G., Lessler J. The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: Estimation and application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020;172:577–582. doi: 10.7326/M20-0504. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Report of the WHO-China Joint Mission on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) [(accessed on 10 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/who-china-joint-mis....
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020. [(accessed on 14 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

